17 KiB
Up: Readme.md, Prev: Section 11, Next: Section 13
Functions in TfeTextView
In this section I will explain functions in TfeTextView object.
tfe.h and tfetextview.h
tfe.h is a top header file and it includes gtk.h and all the header files.
C source files tfeapplication.c and tfenotebook.c include tfe.h at the beginning.
1 #include <gtk/gtk.h>
2
3 #include "../tfetextview/tfetextview.h"
4 #include "tfenotebook.h"
../tfetextview/tfetextview.h is a header file which describes the public functions in tfetextview.c.
1 #ifndef __TFE_TEXT_VIEW_H__
2 #define __TFE_TEXT_VIEW_H__
3
4 #include <gtk/gtk.h>
5
6 #define TFE_TYPE_TEXT_VIEW tfe_text_view_get_type ()
7 G_DECLARE_FINAL_TYPE (TfeTextView, tfe_text_view, TFE, TEXT_VIEW, GtkTextView)
8
9 /* "open-response" signal response */
10 enum TfeTextViewOpenResponseType
11 {
12 TFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_SUCCESS,
13 TFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_CANCEL,
14 TFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_ERROR
15 };
16
17 GFile *
18 tfe_text_view_get_file (TfeTextView *tv);
19
20 void
21 tfe_text_view_open (TfeTextView *tv, GtkWidget *win);
22
23 void
24 tfe_text_view_save (TfeTextView *tv);
25
26 void
27 tfe_text_view_saveas (TfeTextView *tv);
28
29 GtkWidget *
30 tfe_text_view_new_with_file (GFile *file);
31
32 GtkWidget *
33 tfe_text_view_new (void);
34
35 #endif /* __TFE_TEXT_VIEW_H__ */
- 1,2,35: Thanks to these three lines, the following lines are included only once.
- 4: Includes gtk4 header files.
The header file
gtk4also has the same mechanism to avoid including it multiple times. - 6-7: These two lines define TfeTextView.
- 9-15: A definition of the value of the parameter of "open-response" signal.
- 17-33: Declaration of public functions on GtkTextView.
Functions to generate TfeTextView object
TfeTextView Object is generated by tfe_text_view_new or tfe_text_view_new_with_file.
GtkWidget *tfe_text_view_new (void);
tfe_text_view_new just generates a new TfeTextView object and returns the pointer to the new object.
GtkWidget *tfe_text_view_new_with_file (GFile *file);
tfe_text_view_new_with_file is given a Gfile object as the argument and it loads the file into the GtkTextBuffer object, then returns the pointer to the new object.
If an error occurs during the generation process, NULL is returned.
Each function is defined as follows.
1 GtkWidget *
2 tfe_text_view_new_with_file (GFile *file) {
3 g_return_val_if_fail (G_IS_FILE (file), NULL);
4
5 GtkWidget *tv;
6 GtkTextBuffer *tb;
7 char *contents;
8 gsize length;
9
10 if (! g_file_load_contents (file, NULL, &contents, &length, NULL, NULL)) /* read error */
11 return NULL;
12
13 tv = tfe_text_view_new();
14 tb = gtk_text_view_get_buffer (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
15 gtk_text_buffer_set_text (tb, contents, length);
16 g_free (contents);
17 TFE_TEXT_VIEW (tv)->file = g_file_dup (file);
18 return tv;
19 }
20
21 GtkWidget *
22 tfe_text_view_new (void) {
23 return GTK_WIDGET (g_object_new (TFE_TYPE_TEXT_VIEW, NULL));
24 }
- 21-24:
tfe_text_view_newfunction. Just returns the value from the functiong_object_newbut casts it to the pointer to GtkWidget. Initialization is done intfe_text_view_initwhich is called in the process ofg_object_newfunction. - 1-19:
tfe_text_view_new_with_filefunction. - 3:
g_return_val_if_failis described in Glib API reference. It tests whether the argumentfileis a pointer to GFile. If it's true, then the program goes on to the next line. If it's false, then it returns NULL (the second argument) immediately. And at the same time it logs out the error message (usually the log is outputted to stderr or stdout). This function is used to check the programmer's error. If an error occurs, the solution is usually to change the (caller) program and fix the bug. You need to distinguish programmer's errors and runtime errors. You shouldn't use this function to find runtime errors. - 10-11: If an error occurs when reading the file, then return NULL.
- 13: Calls the function
tfe_text_view_new. The function generates TfeTextView instance and returns the pointer to the instance. - 14: Gets the pointer to GtkTextBuffer corresponds to
tv. The pointer is assigned totb - 15: Assigns the contents read from the file to GtkTextBuffer pointed by
tb. - 16: Frees the memories pointed by
contents. - 17: Duplicates
fileand setstv->fileto point it. - 18: Returns
tv, which is a pointer to the newly created TfeTextView instance..
Save and saveas functions
Save and saveas functions write the contents in GtkTextBuffer to a file.
void tfe_text_view_save (TfeTextView *tv)
The function save writes the contents in GtkTextBuffer to a file specified by tv->file.
If tv->file is NULL, then it shows GtkFileChooserDialog and prompts the user to choose a file to save.
Then it saves the contents to the file and sets tv->file to point the GFile instance of the file.
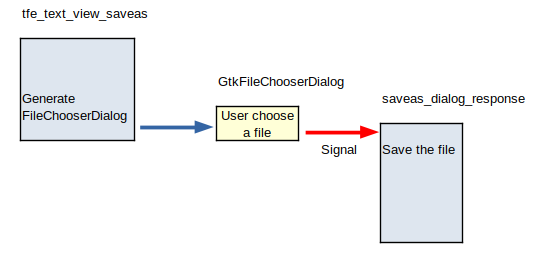
void tfe_text_view_saveas (TfeTextView *tv)
The function saveas uses GtkFileChooserDialog and prompts the user to select a existed file or specify a new file to save.
Then, the function changes tv->file and save the contents to the specified file.
If an error occurs, it is shown to the user through the message dialog.
The error is managed only in the TfeTextView instance and no information is notified to the caller.
1 static void
2 saveas_dialog_response (GtkWidget *dialog, gint response, TfeTextView *tv) {
3 GtkTextBuffer *tb = gtk_text_view_get_buffer (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
4 GFile *file;
5
6 if (response == GTK_RESPONSE_ACCEPT) {
7 file = gtk_file_chooser_get_file (GTK_FILE_CHOOSER (dialog));
8 if (G_IS_FILE(file)) {
9 if (G_IS_FILE (tv->file))
10 g_object_unref (tv->file);
11 tv->file = file;
12 gtk_text_buffer_set_modified (tb, TRUE);
13 g_signal_emit (tv, tfe_text_view_signals[CHANGE_FILE], 0);
14 tfe_text_view_save (TFE_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
15 }
16 }
17 gtk_window_destroy (GTK_WINDOW (dialog));
18 }
19
20 void
21 tfe_text_view_save (TfeTextView *tv) {
22 g_return_if_fail (TFE_IS_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
23
24 GtkTextBuffer *tb = gtk_text_view_get_buffer (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
25 GtkTextIter start_iter;
26 GtkTextIter end_iter;
27 gchar *contents;
28 GtkWidget *message_dialog;
29 GtkWidget *win = gtk_widget_get_ancestor (GTK_WIDGET (tv), GTK_TYPE_WINDOW);
30 GError *err = NULL;
31
32 if (! gtk_text_buffer_get_modified (tb))
33 return; /* no need to save it */
34 else if (tv->file == NULL)
35 tfe_text_view_saveas (tv);
36 else {
37 gtk_text_buffer_get_bounds (tb, &start_iter, &end_iter);
38 contents = gtk_text_buffer_get_text (tb, &start_iter, &end_iter, FALSE);
39 if (g_file_replace_contents (tv->file, contents, strlen (contents), NULL, TRUE, G_FILE_CREATE_NONE, NULL, NULL, &err))
40 gtk_text_buffer_set_modified (tb, FALSE);
41 else {
42 /* It is possible that tv->file is broken or you don't have permission to write. */
43 /* It is a good idea to set tv->file to NULL. */
44 if (G_IS_FILE (tv->file))
45 g_object_unref (tv->file);
46 tv->file =NULL;
47 g_signal_emit (tv, tfe_text_view_signals[CHANGE_FILE], 0);
48 message_dialog = gtk_message_dialog_new (GTK_WINDOW (win), GTK_DIALOG_MODAL,
49 GTK_MESSAGE_ERROR, GTK_BUTTONS_CLOSE,
50 "%s.\n", err->message);
51 g_signal_connect (message_dialog, "response", G_CALLBACK (gtk_window_destroy), NULL);
52 gtk_widget_show (message_dialog);
53 g_error_free (err);
54 }
55 }
56 }
57
58 void
59 tfe_text_view_saveas (TfeTextView *tv) {
60 g_return_if_fail (TFE_IS_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
61
62 GtkWidget *dialog;
63 GtkWidget *win = gtk_widget_get_ancestor (GTK_WIDGET (tv), GTK_TYPE_WINDOW);
64
65 dialog = gtk_file_chooser_dialog_new ("Save file", GTK_WINDOW (win), GTK_FILE_CHOOSER_ACTION_SAVE,
66 "Cancel", GTK_RESPONSE_CANCEL,
67 "Save", GTK_RESPONSE_ACCEPT,
68 NULL);
69 g_signal_connect (dialog, "response", G_CALLBACK (saveas_dialog_response), tv);
70 gtk_widget_show (dialog);
71 }
- 20-56:
Tfe_text_view_savefunction. - 22: If
tvis not a pointer to TfeTextView, then it logs an error message and immediately returns. This function is similar tog_return_val_if_failfunction, but no value is returned becausetfe_text_view_savedoesn't return a value. - 32-33: If the buffer hasn't modified, then it doesn't need to save it. So the function returns.
- 34-35: If
tv->fileis NULL, no file has given yet. It callstfe_text_view_saveaswhich prompts a user to select a file or specify a new file to save. - 37-38: Gets the contents of the GtkTextBuffer and sets
contentsto point it. - 39-40: Saves the content to the file. If it succeeds, it resets the modified bit in the GtkTextBuffer.
- 42-53: If file writing fails, it assigns NULL to
tv->file. Emits "change-file" signal. Shows the error message dialog (48-52). Because the handler isgtk_window_destroy, the dialog disappears when user clicks on the button in the dialog. Frees the GError object. - 58-71:
tfe_text_view_saveasfunction. It shows GtkFileChooserDialog and prompts the user to choose a file. - 65-68: Generates GtkFileChooserDialog.
The title is "Save file".
Transient parent of the dialog is
win, which is the top level window. The action is save mode. The buttons are Cancel and Save. - 69: connects the "response" signal of the dialog and
saveas_dialog_responsehandler. - 1-18:
saveas_dialog_responsesignal handler. - 6-16: If the response is
GTK_RESPONSE_ACCEPT, then it gets a pointer to the GFile object. Then, it setstv->fileto point the GFile. And turns on the modified bit of the GtkTextBuffer, emits "change-file" signal. Finally, it callstfe_text_view_saveto save the buffer to the file.
When you use GtkFileChooserDialog, you need to divide the program into two parts.
One is are a function which generates GtkFileChooserDialog and the other is a signal handler.
The function just generates and shows GtkFileChooserDialog.
The rest is done by the handler.
It gets Gfile from GtkFileChooserDialog and saves the buffer to the file by calling tfe_text_view_save.
Open function
Open function shows GtkFileChooserDialog to users and prompts them to choose a file. Then it reads the file and puts the text to GtkTextBuffer.
void tfe_text_view_open (TfeTextView *tv, GtkWidget *win);
The parameter win is the top window.
It will be a transient parent window of GtkFileChooserDialog when the dialog is generated..
This allows window managers to keep the dialog on top of the parent window, or center the dialog over the parent window.
It is possible to give no parent window to the dialog.
However, it is encouraged to give a parent window to dialog.
This function might be called just after tv has been generated.
In that case, tv has not been incorporated into the widget hierarchy.
Therefore it is impossible to get the top window from tv.
That's why the function needs win parameter.
This function is usually called when the buffer of tv is empty.
However, even if the buffer is not empty, tfe_text_view_open doesn't treat it as an error.
If you want to revert the buffer, calling this function is appropriate.
Otherwise probably bad things will happen.
1 static void
2 open_dialog_response(GtkWidget *dialog, gint response, TfeTextView *tv) {
3 GtkTextBuffer *tb = gtk_text_view_get_buffer (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
4 GFile *file;
5 char *contents;
6 gsize length;
7 GtkWidget *message_dialog;
8 GError *err = NULL;
9
10 if (response != GTK_RESPONSE_ACCEPT)
11 g_signal_emit (tv, tfe_text_view_signals[OPEN_RESPONSE], 0, TFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_CANCEL);
12 else if (! G_IS_FILE (file = gtk_file_chooser_get_file (GTK_FILE_CHOOSER (dialog))))
13 g_signal_emit (tv, tfe_text_view_signals[OPEN_RESPONSE], 0, TFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_ERROR);
14 else if (! g_file_load_contents (file, NULL, &contents, &length, NULL, &err)) { /* read error */
15 if (G_IS_FILE (file))
16 g_object_unref (file);
17 message_dialog = gtk_message_dialog_new (GTK_WINDOW (dialog), GTK_DIALOG_MODAL,
18 GTK_MESSAGE_ERROR, GTK_BUTTONS_CLOSE,
19 "%s.\n", err->message);
20 g_signal_connect (message_dialog, "response", G_CALLBACK (gtk_window_destroy), NULL);
21 gtk_widget_show (message_dialog);
22 g_error_free (err);
23 g_signal_emit (tv, tfe_text_view_signals[OPEN_RESPONSE], 0, TFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_ERROR);
24 } else {
25 gtk_text_buffer_set_text (tb, contents, length);
26 g_free (contents);
27 if (G_IS_FILE (tv->file))
28 g_object_unref (tv->file);
29 tv->file = file;
30 gtk_text_buffer_set_modified (tb, FALSE);
31 g_signal_emit (tv, tfe_text_view_signals[OPEN_RESPONSE], 0, TFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_SUCCESS);
32 g_signal_emit (tv, tfe_text_view_signals[CHANGE_FILE], 0);
33 }
34 gtk_window_destroy (GTK_WINDOW (dialog));
35 }
36
37 void
38 tfe_text_view_open (TfeTextView *tv, GtkWidget *win) {
39 g_return_if_fail (TFE_IS_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
40 g_return_if_fail (GTK_IS_WINDOW (win));
41
42 GtkWidget *dialog;
43
44 dialog = gtk_file_chooser_dialog_new ("Open file", GTK_WINDOW (win), GTK_FILE_CHOOSER_ACTION_OPEN,
45 "Cancel", GTK_RESPONSE_CANCEL,
46 "Open", GTK_RESPONSE_ACCEPT,
47 NULL);
48 g_signal_connect (dialog, "response", G_CALLBACK (open_dialog_response), tv);
49 gtk_widget_show (dialog);
50 }
- 37-50:
tfe_text_view_openfunction. - 44-47: Generates GtkFileChooserDialog. The title is "Open file". Transient parent window is the top window of the application, which is given by the caller. The action is open mode. The buttons are Cancel and Open.
- 48: connects the "response" signal of the dialog and
open_dialog_responsesignal handler. - 49: Shows the dialog.
- 1-35:
open_dialog_responsesignal handler. - 10-11: If the response from GtkFileChooserDialog is not
GTK_RESPONSE_ACCEPT, which means the user has clicked on the "Cancel" button or close button, then it emits "open-response" signal with the parameterTFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_CANCEL. - 12-13: Gets a pointer to Gfile by
gtk_file_chooser_get_file. If it is not GFile, maybe an error occurred. Then it emits "open-response" signal with the parameterTFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_ERROR. - 14-23: If an error occurs at file reading, then it decreases the reference count of the Gfile, shows a message dialog to report the error to the user and emits "open-response" signal with the parameter
TFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_ERROR. - 24-33: If the file has successfully read, then the text is inserted to GtkTextBuffer, frees the temporary buffer pointed by
contentsand setstv->fileto point the file (no duplication or unref is not necessary). Then, it emits "open-response" signal with the parameterTFE_OPEN_RESPONSE_SUCCESSand emits "change-file" signal. - 34: closes GtkFileCooserDialog.
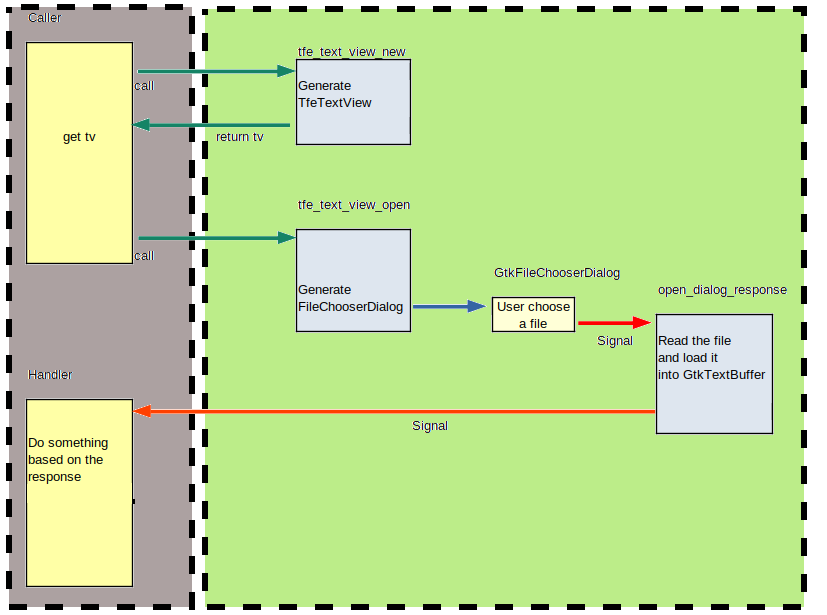
Now let's think about the whole process between the other object (caller) and TfeTextView.
It is shown in the following diagram and you would think that it is really complicated.
Because signal is the only way for GtkFileChooserDialog to communicate with others.
In Gtk3, gtk_dialog_run function is available.
It simplifies the process.
However, in Gtk4, gtk_dialog_runis unavailable any more.
- A caller gets a pointer
tvto TfeTextView by callingtfe_text_view_new. - The caller connects the handler (left bottom in the diagram) and the signal "open-response".
- It calls
tfe_text_view_opento prompt the user to select a file from GtkFileChooserDialog. - The dialog emits a signal and it invokes the handler
open_dialog_response. - The handler reads the file and inserts the text into GtkTextBuffer and emits a signal to inform the response status.
- The handler outside TfeTextView receives the signal.
Get file function
gtk_text_view_get_file is a simple function show as follows.
1 GFile *
2 tfe_text_view_get_file (TfeTextView *tv) {
3 g_return_val_if_fail (TFE_IS_TEXT_VIEW (tv), NULL);
4
5 return g_file_dup (tv->file);
6 }
The important thing is to duplicate tv->file.
Otherwise, if the caller frees the GFile object, tv->file is no more guaranteed to point the GFile.
Source file of tfetextview.c
All the source files are listed in Section 15. You can find them under src/tfe5 and src/tfetextview directories.
Up: Readme.md, Prev: Section 11, Next: Section 13