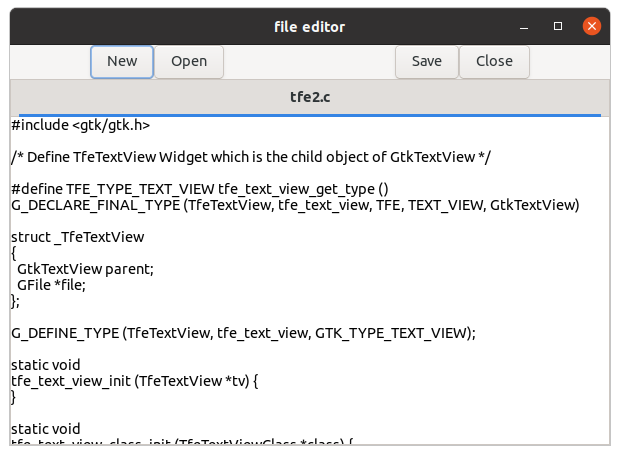
18 KiB
Up: README.md, Prev: Section 8, Next: Section 10
GtkBuilder and UI file
New, Open and Save button
We made very simple editor in the previous section. It reads files at the start and writes them out at the end of the program. It works, but is not so good. It would be better if we had "New", "Open", "Save" and "Close" buttons. This section describes how to put those buttons into the window.
The screenshot above shows the layout.
The function app_open in the source code tfe2.c is as follows.
1 static void
2 app_open (GApplication *app, GFile ** files, gint n_files, gchar *hint) {
3 GtkWidget *win;
4 GtkWidget *nb;
5 GtkWidget *lab;
6 GtkNotebookPage *nbp;
7 GtkWidget *scr;
8 GtkWidget *tv;
9 GtkTextBuffer *tb;
10 char *contents;
11 gsize length;
12 char *filename;
13 int i;
14
15 GtkWidget *boxv;
16 GtkWidget *boxh;
17 GtkWidget *dmy1;
18 GtkWidget *dmy2;
19 GtkWidget *dmy3;
20 GtkWidget *btnn; /* button for new */
21 GtkWidget *btno; /* button for open */
22 GtkWidget *btns; /* button for save */
23 GtkWidget *btnc; /* button for close */
24
25 win = gtk_application_window_new (GTK_APPLICATION (app));
26 gtk_window_set_title (GTK_WINDOW (win), "file editor");
27 gtk_window_set_default_size (GTK_WINDOW (win), 600, 400);
28
29 boxv = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_VERTICAL, 0);
30 gtk_window_set_child (GTK_WINDOW (win), boxv);
31
32 boxh = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_HORIZONTAL, 0);
33 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxv), boxh);
34
35 dmy1 = gtk_label_new(NULL); /* dummy label for left space */
36 gtk_label_set_width_chars (GTK_LABEL (dmy1), 10);
37 dmy2 = gtk_label_new(NULL); /* dummy label for center space */
38 gtk_widget_set_hexpand (dmy2, TRUE);
39 dmy3 = gtk_label_new(NULL); /* dummy label for right space */
40 gtk_label_set_width_chars (GTK_LABEL (dmy3), 10);
41 btnn = gtk_button_new_with_label ("New");
42 btno = gtk_button_new_with_label ("Open");
43 btns = gtk_button_new_with_label ("Save");
44 btnc = gtk_button_new_with_label ("Close");
45
46 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), dmy1);
47 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), btnn);
48 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), btno);
49 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), dmy2);
50 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), btns);
51 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), btnc);
52 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), dmy3);
53
54 nb = gtk_notebook_new ();
55 gtk_widget_set_hexpand (nb, TRUE);
56 gtk_widget_set_vexpand (nb, TRUE);
57 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxv), nb);
58
59 for (i = 0; i < n_files; i++) {
60 if (g_file_load_contents (files[i], NULL, &contents, &length, NULL, NULL)) {
61 scr = gtk_scrolled_window_new ();
62 tv = tfe_text_view_new ();
63 tb = gtk_text_view_get_buffer (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
64 gtk_text_view_set_wrap_mode (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv), GTK_WRAP_WORD_CHAR);
65 gtk_scrolled_window_set_child (GTK_SCROLLED_WINDOW (scr), tv);
66
67 tfe_text_view_set_file (TFE_TEXT_VIEW (tv), g_file_dup (files[i]));
68 gtk_text_buffer_set_text (tb, contents, length);
69 g_free (contents);
70 filename = g_file_get_basename (files[i]);
71 lab = gtk_label_new (filename);
72 gtk_notebook_append_page (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb), scr, lab);
73 nbp = gtk_notebook_get_page (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb), scr);
74 g_object_set (nbp, "tab-expand", TRUE, NULL);
75 g_free (filename);
76 } else if ((filename = g_file_get_path (files[i])) != NULL) {
77 g_print ("No such file: %s.\n", filename);
78 g_free (filename);
79 } else
80 g_print ("No valid file is given\n");
81 }
82 if (gtk_notebook_get_n_pages (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb)) > 0) {
83 gtk_window_present (GTK_WINDOW (win));
84 } else
85 gtk_window_destroy (GTK_WINDOW (win));
86 }
The function app_open builds the widgets in the main application window.
- 25-27: Creates a GtkApplicationWindow instance and sets the title and default size.
- 29-30: Creates a GtkBox instance
boxv. It is a vertical box and a child of GtkApplicationWindow. It has two children. The first child is a horizontal box. The second child is a GtkNotebook. - 32-33: Creates a GtkBox instance
boxhand appends it toboxvas a first child. - 35-40: Creates three dummy labels.
The labels
dmy1anddmy3has a character width of ten. The other labeldmy2has hexpand property which is set to be TRUE. This makes the label expands horizontally as long as possible. - 41-44: Creates four buttons.
- 46-52: Appends these GtkLabel and GtkButton to
boxh. - 54-57: Creates a GtkNotebook instance and sets hexpand and vexpand properties to be TRUE.
This makes it expand horizontally and vertically as big as possible.
It is appended to
boxvas the second child.
The number of widget-build lines is 33(=57-25+1).
We also needed many variables (boxv, boxh, dmy1, ...) and most of them used only for building the widgets.
Are there any good solution to reduce these work?
Gtk provides GtkBuilder. It reads user interface (UI) data and builds a window. It reduces this cumbersome work.
The UI File
Look at the UI file tfe3.ui that defines widget structure.
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2 <interface>
3 <object class="GtkApplicationWindow" id="win">
4 <property name="title">file editor</property>
5 <property name="default-width">600</property>
6 <property name="default-height">400</property>
7 <child>
8 <object class="GtkBox" id="boxv">
9 <property name="orientation">GTK_ORIENTATION_VERTICAL</property>
10 <child>
11 <object class="GtkBox" id="boxh">
12 <property name="orientation">GTK_ORIENTATION_HORIZONTAL</property>
13 <child>
14 <object class="GtkLabel" id="dmy1">
15 <property name="width-chars">10</property>
16 </object>
17 </child>
18 <child>
19 <object class="GtkButton" id="btnn">
20 <property name="label">New</property>
21 </object>
22 </child>
23 <child>
24 <object class="GtkButton" id="btno">
25 <property name="label">Open</property>
26 </object>
27 </child>
28 <child>
29 <object class="GtkLabel" id="dmy2">
30 <property name="hexpand">TRUE</property>
31 </object>
32 </child>
33 <child>
34 <object class="GtkButton" id="btns">
35 <property name="label">Save</property>
36 </object>
37 </child>
38 <child>
39 <object class="GtkButton" id="btnc">
40 <property name="label">Close</property>
41 </object>
42 </child>
43 <child>
44 <object class="GtkLabel" id="dmy3">
45 <property name="width-chars">10</property>
46 </object>
47 </child>
48 </object>
49 </child>
50 <child>
51 <object class="GtkNotebook" id="nb">
52 <property name="hexpand">TRUE</property>
53 <property name="vexpand">TRUE</property>
54 </object>
55 </child>
56 </object>
57 </child>
58 </object>
59 </interface>
The is a XML file.
Tags begin with < and end with >.
There are two types of tags, the start tag and the end tag.
For example, <interface> is a start tag and </interface> is an end tag.
The UI file begins and ends with interface tags.
Some tags, for example object tags, can have a class and id attributes in their start tag.
- 1: XML declaration. It specifies that the XML version is 1.0 and the encoding is UTF-8.
- 3-6: An object tag with
GtkApplicationWindowclass andwinid. This is the top level window. And the three properties of the window are defined. Thetitleproperty is "file editor",default-widthproperty is 600 anddefault-heightproperty is 400. - 7: child tag means a child widget.
For example, line 7 tells us that GtkBox object with "boxv" id attribute is a child widget of
win.
Compare this ui file and the lines 25-57 in the tfe2.c source code.
Both builds the same window with its descendant widgets.
You can check the ui file with gtk4-builder-tool.
gtk4-builder-tool validate <ui file name>validates the ui file. If the ui file includes some syntactical error,gtk4-builder-toolprints the error.gtk4-builder-tool simplify <ui file name>simplifies the ui file and prints the result. If--replaceoption is given, it replaces the ui file with the simplified one. If the ui file specifies a value of property but it is default, then it will be removed. And some values are simplified. For example, "TRUE"and "FALSE" becomes "1" and "0" respectively. However, "TRUE" or "FALSE" is better for maintenance.
It is a good idea to check your ui file before compiling.
GtkBuilder
GtkBuilder builds widgets based on a ui file.
GtkBuilder *build;
build = gtk_builder_new_from_file ("tfe3.ui");
win = GTK_WIDGET (gtk_builder_get_object (build, "win"));
gtk_window_set_application (GTK_WINDOW (win), GTK_APPLICATION (app));
nb = GTK_WIDGET (gtk_builder_get_object (build, "nb"));
The function gtk_builder_new_from_file reads the file given as an argument.
Then, it builds the widgets and creates GtkBuilder object.
The function gtk_builder_get_object (build, "win") returns the pointer to the widget win, which is the id in the ui file.
All the widgets are connected based on the parent-children relationship described in the ui file.
We only need win and nb for the program below.
This reduces lines in the C source file.
$ cd tfe; diff tfe2.c tfe3.c
58a59
> GtkBuilder *build;
60,103c61,65
< GtkWidget *boxv;
< GtkWidget *boxh;
< GtkWidget *dmy1;
< GtkWidget *dmy2;
< GtkWidget *dmy3;
< GtkWidget *btnn; /* button for new */
< GtkWidget *btno; /* button for open */
< GtkWidget *btns; /* button for save */
< GtkWidget *btnc; /* button for close */
<
< win = gtk_application_window_new (GTK_APPLICATION (app));
< gtk_window_set_title (GTK_WINDOW (win), "file editor");
< gtk_window_set_default_size (GTK_WINDOW (win), 600, 400);
<
< boxv = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_VERTICAL, 0);
< gtk_window_set_child (GTK_WINDOW (win), boxv);
<
< boxh = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_HORIZONTAL, 0);
< gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxv), boxh);
<
< dmy1 = gtk_label_new(NULL); /* dummy label for left space */
< gtk_label_set_width_chars (GTK_LABEL (dmy1), 10);
< dmy2 = gtk_label_new(NULL); /* dummy label for center space */
< gtk_widget_set_hexpand (dmy2, TRUE);
< dmy3 = gtk_label_new(NULL); /* dummy label for right space */
< gtk_label_set_width_chars (GTK_LABEL (dmy3), 10);
< btnn = gtk_button_new_with_label ("New");
< btno = gtk_button_new_with_label ("Open");
< btns = gtk_button_new_with_label ("Save");
< btnc = gtk_button_new_with_label ("Close");
<
< gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), dmy1);
< gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), btnn);
< gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), btno);
< gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), dmy2);
< gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), btns);
< gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), btnc);
< gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxh), dmy3);
<
< nb = gtk_notebook_new ();
< gtk_widget_set_hexpand (nb, TRUE);
< gtk_widget_set_vexpand (nb, TRUE);
< gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (boxv), nb);
<
---
> build = gtk_builder_new_from_file ("tfe3.ui");
> win = GTK_WIDGET (gtk_builder_get_object (build, "win"));
> gtk_window_set_application (GTK_WINDOW (win), GTK_APPLICATION (app));
> nb = GTK_WIDGET (gtk_builder_get_object (build, "nb"));
> g_object_unref(build);
138c100
< app = gtk_application_new ("com.github.ToshioCP.tfe2", G_APPLICATION_HANDLES_OPEN);
---
> app = gtk_application_new ("com.github.ToshioCP.tfe3", G_APPLICATION_HANDLES_OPEN);
144a107
>
60,103c61,65 means 44 (=103-60+1) lines are changed to 5 (=65-61+1) lines.
Therefore, 39 lines are reduced.
Using ui file not only shortens C source files, but also makes the widgets' structure clear.
Now I'll show you app_open function in the C file tfe3.c.
1 static void
2 app_open (GApplication *app, GFile ** files, gint n_files, gchar *hint) {
3 GtkWidget *win;
4 GtkWidget *nb;
5 GtkWidget *lab;
6 GtkNotebookPage *nbp;
7 GtkWidget *scr;
8 GtkWidget *tv;
9 GtkTextBuffer *tb;
10 char *contents;
11 gsize length;
12 char *filename;
13 int i;
14 GtkBuilder *build;
15
16 build = gtk_builder_new_from_file ("tfe3.ui");
17 win = GTK_WIDGET (gtk_builder_get_object (build, "win"));
18 gtk_window_set_application (GTK_WINDOW (win), GTK_APPLICATION (app));
19 nb = GTK_WIDGET (gtk_builder_get_object (build, "nb"));
20 g_object_unref(build);
21 for (i = 0; i < n_files; i++) {
22 if (g_file_load_contents (files[i], NULL, &contents, &length, NULL, NULL)) {
23 scr = gtk_scrolled_window_new ();
24 tv = tfe_text_view_new ();
25 tb = gtk_text_view_get_buffer (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
26 gtk_text_view_set_wrap_mode (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv), GTK_WRAP_WORD_CHAR);
27 gtk_scrolled_window_set_child (GTK_SCROLLED_WINDOW (scr), tv);
28
29 tfe_text_view_set_file (TFE_TEXT_VIEW (tv), g_file_dup (files[i]));
30 gtk_text_buffer_set_text (tb, contents, length);
31 g_free (contents);
32 filename = g_file_get_basename (files[i]);
33 lab = gtk_label_new (filename);
34 gtk_notebook_append_page (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb), scr, lab);
35 nbp = gtk_notebook_get_page (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb), scr);
36 g_object_set (nbp, "tab-expand", TRUE, NULL);
37 g_free (filename);
38 } else if ((filename = g_file_get_path (files[i])) != NULL) {
39 g_print ("No such file: %s.\n", filename);
40 g_free (filename);
41 } else
42 g_print ("No valid file is given\n");
43 }
44 if (gtk_notebook_get_n_pages (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb)) > 0) {
45 gtk_window_present (GTK_WINDOW (win));
46 } else
47 gtk_window_destroy (GTK_WINDOW (win));
48 }
The whole source code of tfe3.c is stored in src/tfe directory.
Using ui string
GtkBuilder can build widgets with string.
Use gtk_builder_new_from_string instead of gtk_builder_new_from_file.
char *uistring;
uistring =
"<interface>"
"<object class="GtkApplicationWindow" id="win">"
"<property name=\"title\">file editor</property>"
"<property name=\"default-width\">600</property>"
"<property name=\"default-height\">400</property>"
"<child>"
"<object class=\"GtkBox\" id=\"boxv\">"
"<property name="orientation">GTK_ORIENTATION_VERTICAL</property>"
... ... ...
... ... ...
"</interface>";
build = gtk_builder_new_from_string (uistring, -1);
This method has an advantage and disadvantage. The advantage is that the ui string is written in the source code. So, no ui file is needed on runtime. The disadvantage is that writing C string is a bit bothersome because of the double quotes. If you want to use this method, you should write a script that transforms ui file into C-string.
- Add backslash before each double quote.
- Add double quotes at the left and right of the string in each line.
Gresource
Using Gresource is similar to using string. But Gresource is compressed binary data, not text data. And there's a compiler that compiles ui file into Gresource. It can compile not only text files but also binary files such as images, sounds and so on. And after compilation, it bundles them up into one Gresource object.
An xml file is necessary for the resource compiler glib-compile-resources.
It describes resource files.
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2 <gresources>
3 <gresource prefix="/com/github/ToshioCP/tfe3">
4 <file>tfe3.ui</file>
5 </gresource>
6 </gresources>
- 2:
gresourcestag can include multiple gresources (gresource tags). However, this xml has only one gresource. - 3: The gresource has a prefix
/com/github/ToshioCP/tfe3. - 4: The name of the gresource is
tfe3.ui. The resource will be pointed with/com/github/ToshioCP/tfe3/tfe3.uiby GtkBuilder. The pattern is "prefix" + "name". If you want to add more files, insert them between line 4 and 5.
Save this xml text to tfe3.gresource.xml.
The gresource compiler glib-compile-resources shows its usage with the argument --help.
$ LANG=C glib-compile-resources --help
Usage:
glib-compile-resources [OPTION?] FILE
Compile a resource specification into a resource file.
Resource specification files have the extension .gresource.xml,
and the resource file have the extension called .gresource.
Help Options:
-h, --help Show help options
Application Options:
--version Show program version and exit
--target=FILE Name of the output file
--sourcedir=DIRECTORY The directories to load files referenced in FILE from (default: current directory)
--generate Generate output in the format selected for by the target filename extension
--generate-header Generate source header
--generate-source Generate source code used to link in the resource file into your code
--generate-dependencies Generate dependency list
--dependency-file=FILE Name of the dependency file to generate
--generate-phony-targets Include phony targets in the generated dependency file
--manual-register Don?t automatically create and register resource
--internal Don?t export functions; declare them G_GNUC_INTERNAL
--external-data Don?t embed resource data in the C file; assume it's linked externally instead
--c-name C identifier name used for the generated source code
-C, --compiler The target C compiler (default: the CC environment variable)
Now run the compiler.
$ glib-compile-resources tfe3.gresource.xml --target=resources.c --generate-source
Then a C source file resources.c is generated.
Modify tfe3.c and save it as tfe3_r.c.
#include "resources.c"
... ... ...
... ... ...
build = gtk_builder_new_from_resource ("/com/github/ToshioCP/tfe3/tfe3.ui");
... ... ...
... ... ...
The function gtk_builder_new_from_resource builds widgets from a resource.
Then, compile and run it. A window appears and it is the same as the screenshot at the beginning of this page.
Generally, resource is the best way for C language. If you use other languages like Ruby, string is better than resource.
Up: README.md, Prev: Section 8, Next: Section 10