24 KiB
Up: Readme.md, Prev: Section 25
GtkExpression
GtkExpression is a fundamental type. It is not a descendant of GObject. GtkExpression provides a way to describe references to values. GtkExpression needs to be evaluated to obtain a value.
It is similar to arithmetic calculation.
1 + 2 = 3
1+2 is an expression.
It shows the way how to calculate.
3 is the value comes from the expression.
Evaluation is to calculate the expression and get the value.
GtkExpression is a way to get a value. Evaluation is like a calculation. A value is got by evaluating the expression.
First, I want to show you the C file of the example for GtkExpression.
Its name is exp.c and located under src/expression directory.
You don't need to understand the details now, just look at it.
It will be explained in the next subsection.
1 #include <gtk/gtk.h>
2
3 GtkWidget *win1;
4 int width, height;
5 GtkExpressionWatch *watch_width;
6 GtkExpressionWatch *watch_height;
7
8 /* Notify is called when "default-width" or "default-height" property is changed. */
9 static void
10 notify (gpointer user_data) {
11 GValue value = G_VALUE_INIT;
12 char *title;
13
14 if (watch_width && gtk_expression_watch_evaluate (watch_width, &value))
15 width = g_value_get_int (&value);
16 g_value_unset (&value);
17 if (watch_height && gtk_expression_watch_evaluate (watch_height, &value))
18 height = g_value_get_int (&value);
19 g_value_unset (&value);
20 title = g_strdup_printf ("%d x %d", width, height);
21 gtk_window_set_title (GTK_WINDOW (win1), title);
22 g_free (title);
23 }
24
25 /* This function is used by closure tag in exp.ui. */
26 char *
27 set_title (GtkWidget *win, int width, int height) {
28 return g_strdup_printf ("%d x %d", width, height);
29 }
30
31 /* ----- activate, open, startup handlers ----- */
32 static void
33 app_activate (GApplication *application) {
34 GtkApplication *app = GTK_APPLICATION (application);
35 GtkWidget *box;
36 GtkWidget *label1, *label2, *label3;
37 GtkWidget *entry;
38 GtkEntryBuffer *buffer;
39 GtkBuilder *build;
40 GtkExpression *expression, *expression1, *expression2;
41 GtkExpressionWatch *watch;
42 GValue value = G_VALUE_INIT;
43 char *s;
44
45 /* Creates GtkApplicationWindow instance. */
46 /* The codes below are complecated. It does the same as "win1 = gtk_application_window_new (app);". */
47 /* The codes are written just to show how to use GtkExpression. */
48 expression = gtk_cclosure_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_APPLICATION_WINDOW, NULL, 0, NULL,
49 G_CALLBACK (gtk_application_window_new), NULL, NULL);
50 if (gtk_expression_evaluate (expression, app, &value)) {
51 win1 = GTK_WIDGET (g_value_get_object (&value)); /* GtkApplicationWindow */
52 g_object_ref (win1);
53 g_print ("Got GtkApplicationWindow object.\n");
54 }else
55 g_print ("The cclosure expression couldn't be evaluated.\n");
56 gtk_expression_unref (expression);
57 g_value_unset (&value); /* At the same time, the reference count of win1 is decreased by one. */
58
59 /* Builds a window with components */
60 box = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_VERTICAL, 10);
61 label1 = gtk_label_new (NULL);
62 label2 = gtk_label_new (NULL);
63 label3 = gtk_label_new (NULL);
64 buffer = gtk_entry_buffer_new (NULL, 0);
65 entry = gtk_entry_new_with_buffer (buffer);
66 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), label1);
67 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), label2);
68 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), label3);
69 gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), entry);
70 gtk_window_set_child (GTK_WINDOW (win1), box);
71
72 /* Constant expression */
73 expression = gtk_constant_expression_new (G_TYPE_INT,100);
74 if (gtk_expression_evaluate (expression, NULL, &value)) {
75 s = g_strdup_printf ("%d", g_value_get_int (&value));
76 gtk_label_set_text (GTK_LABEL (label1), s);
77 g_free (s);
78 } else
79 g_print ("The constant expression couldn't be evaluated.\n");
80 gtk_expression_unref (expression);
81 g_value_unset (&value);
82
83 /* Property expression and binding*/
84 expression1 = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_ENTRY, NULL, "buffer");
85 expression2 = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_ENTRY_BUFFER, expression1, "text");
86 watch = gtk_expression_bind (expression2, label2, "label", entry);
87
88 /* Constant expression instead of "this" instance */
89 expression1 = gtk_constant_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_APPLICATION, app);
90 expression2 = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_APPLICATION, expression1, "application-id");
91 if (gtk_expression_evaluate (expression2, NULL, &value))
92 gtk_label_set_text (GTK_LABEL (label3), g_value_get_string (&value));
93 else
94 g_print ("The property expression couldn't be evaluated.\n");
95 gtk_expression_unref (expression1); /* expression 2 is also freed. */
96 g_value_unset (&value);
97
98 width = 800;
99 height = 600;
100 gtk_window_set_default_size (GTK_WINDOW (win1), width, height);
101 notify(NULL);
102
103 /* GtkExpressionWatch */
104 expression1 = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_WINDOW, NULL, "default-width");
105 watch_width = gtk_expression_watch (expression1, win1, notify, NULL, NULL);
106 expression2 = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_WINDOW, NULL, "default-height");
107 watch_height = gtk_expression_watch (expression2, win1, notify, NULL, NULL);
108
109 gtk_widget_show (win1);
110
111 /* Builds a window with exp.ui resource */
112 build = gtk_builder_new_from_resource ("/com/github/ToshioCP/exp/exp.ui");
113 GtkWidget *win2 = GTK_WIDGET (gtk_builder_get_object (build, "win2"));
114 gtk_window_set_application (GTK_WINDOW (win2), app);
115 g_object_unref (build);
116
117 gtk_widget_show (win2);
118 }
119
120 static void
121 app_startup (GApplication *application) {
122 }
123
124 #define APPLICATION_ID "com.github.ToshioCP.exp"
125
126 int
127 main (int argc, char **argv) {
128 GtkApplication *app;
129 int stat;
130
131 app = gtk_application_new (APPLICATION_ID, G_APPLICATION_FLAGS_NONE);
132
133 g_signal_connect (app, "startup", G_CALLBACK (app_startup), NULL);
134 g_signal_connect (app, "activate", G_CALLBACK (app_activate), NULL);
135 /* g_signal_connect (app, "open", G_CALLBACK (app_open), NULL);*/
136
137 stat =g_application_run (G_APPLICATION (app), argc, argv);
138 g_object_unref (app);
139 return stat;
140 }
141
exp.c consists of five functions.
notifyset_titleapp_activate. This is a handler of "activate" signal on GtkApplication instance.app_startup. This is a handler of "startup"signal. But nothing is done inexp.c.main. This function is called first.
The role of main, app_startup and app_activate is the same as before.
app_activate is an actual main body in exp.c.
Constant expression
Constant expression provides constant value or instance when it is evaluated.
- 73-81: An example code of a constant expression. It is extracted and put into here.
expression = gtk_constant_expression_new (G_TYPE_INT,100);
if (gtk_expression_evaluate (expression, NULL, &value)) {
s = g_strdup_printf ("%d", g_value_get_int (&value));
gtk_label_set_text (GTK_LABEL (label1), s);
g_free (s);
} else
g_print ("The constant expression couldn't be evaluated.\n");
gtk_expression_unref (expression);
g_value_unset (&value);
- Constant expression is created with
gtk_constant_expression_newfunction. The parameter of the function is a type (GType) and a value (or instance). gtk_expression_evaluateevaluates the expression. It has three parameters, the expression to evaluate,thisinstance and GValue for being set with the value.thisinstance isn't necessary for constant expressions. Therefore the second argument is NULL.gtk_expression_evaluatereturns TRUE if it successfully evaluates the expression. Otherwise it returns FALSE.- If it returns TRUE, the GValue
valueis set with the value of the expression. The type is int so it needs to be converted to a string.g_strdup_printfcreates a new strings. - GtkLabel
label1is set withs. - If the evaluation fails a message is displayed.
- The expression and GValue are freed.
Constant expression is usually used to give a constant value or instance to another expression.
Property expression
Property expression looks up a property in a GObject object. For example, a property expression that refers "label" property in GtkLabel object is created like this.
expression = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_LABEL, another_expression, "label");
another_expression is expected to give a GtkLabel instance when it is evaluated.
For example,
label = gtk_label_new ("Hello");
another_expression = gtk_constant_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_LABEL, label);
expression = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_LABEL, another_expression, "label");
If expression is evaluated, the second parameter another_expression is evaluated in advance.
Then the value of another_expression is label (GtkLabel instance).
Then, expression looks up "label" property of label and the evaluation result is "Hello".
In the example above, the second argument of gtk_property_expression_new is another expression.
But the second argument can be NULL.
If it is NULL, this instance is used instead.
this is given by gtk_expression_evaluate function at the evaluation.
Now look at exp.c.
The lines from 84 to 86 is extracted here.
expression1 = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_ENTRY, NULL, "buffer");
expression2 = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_ENTRY_BUFFER, expression1, "text");
watch = gtk_expression_bind (expression2, label2, "label", entry);
expression1looks up "buffer" property ofthisobject, which isGTK_TYPE_ENTRYtype.expression2looks up "text" property of GtkEntryBuffer object given byepression1.gtk_expression_bindbinds a property to a value given by the expression. In this program, it binds a "label" property inlabel2to the value evaluated withexpresion2withentryasthisobject. The evaluation process is as follows.expression2is evaluated. But it includesexpression1soexpression1is evaluated in advance.- Because the second argument of
expression1is NULL,thisobject is used.thisis given bygtk_expression_bind. It isentry(GtkEntry instance).expression1looks up "buffer" property inentry. It is a GtkEntryBuffer instancebuffer. (See line 64 inexp.c.) - Then,
expression2looks up "text" property inbuffer. It is a text held inentry. - The text is assigned to "label" property in
label2.
gtk_expression_bindcreates a GtkExpressionWatch, which is assigned towatch. It watchesexpression2. And whenever the value fromexpression2changes, it evaluatesexpression2and set "label" property inlabel2. So, the change of the text inentryreflects "label" inlabel2immediately.
closure expression
Closure expression calls closure when it is evaluated.
A closure is a generic representation of a callback (a pointer to a function).
For information about closure, see GObject API reference.
A closure expression is created with gtk_cclosure_expression_new function.
GtkExpression *
gtk_cclosure_expression_new (GType value_type,
GClosureMarshal marshal,
guint n_params,
GtkExpression **params,
GCallback callback_func,
gpointer user_data,
GClosureNotify user_destroy);
value_typeis the type of the value when it is evaluated.marshalis a marshaller. You can assign NULL. If it is NULL, theng_cclosure_marshal_generic ()is used as a marshaller. It is a generic marshaller function implemented via libffi.n_paramsis the number of parameters.paramspoints expressions for each parameter.callback_funcis a callback function.user_datais user data. You can add it for the closure. It is likeuser_dataing_signal_connect. If it is not necessary, assign NULL.user_destroyis a destroy notify foruser_data. It is called to destroyuser_datawhen it is no longer needed. If NULL is assigned touser_data, assign NULL touser_destroy, too.
The following is extracted from exp.c.
It is from line 48 to line 57.
expression = gtk_cclosure_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_APPLICATION_WINDOW, NULL, 0, NULL,
G_CALLBACK (gtk_application_window_new), NULL, NULL);
if (gtk_expression_evaluate (expression, app, &value)) {
win1 = GTK_WIDGET (g_value_get_object (&value)); /* GtkApplicationWindow */
g_object_ref (win1);
g_print ("Got GtkApplicationWindow object.\n");
}else
g_print ("The cclosure expression couldn't be evaluated.\n");
gtk_expression_unref (expression);
g_value_unset (&value); /* At the same time, the reference count of win1 is decreased by one. */
The callback function is gtk_application_window_new.
This function has one parameter which is an instance of GtkApplication.
And it returns newly created GtkApplicationWindow instance.
So, the first argument is GTK_TYPE_APPLICATION_WINDOW which is the type of the return value.
The second argument is NULL so general marshaller g_cclosure_marshal_generic () will be used.
I think assigning NULL works in most cases when you are programming in C language.
The arguments given to the call back function are this object and parameters which are the fourth argument of gtk_cclosure_expression_new.
So, the number of arguments is n_params + 1.
Because gtk_application_window_new has one parameter, so n_params is zero and **params is NULL.
No user data is necessary, so user_data and user_destroy are NULL.
gtk_expression_evaluate evaluates the expression.
this instance will be the first argument for gtk_application_window_new, so it is app.
If the evaluation succeeds, the GValue value holds a newly created GtkApplicationWindow instance.
It is assigned to win1.
The GValue will be unset when it is no longer used.
And when it is unset, the GtkApplicationWindow instance will be released and its reference count will be decreased by one.
It is necessary to increase the reference count by one in advance to keep the instance.
gtk_expression_unref frees expression and value is unset.
As a result, we got a GtkApplicationWindow instance win1.
We can do the same by:
win1 = gtk_application_window_new (app);
The example is more complicated and not practical than this one line code. The aim of the example is just to show how closure expression works.
Closure expression is flexible than other type of expression because you can specify your own callback function.
GtkExpressionWatch
GtkExpressionWatch watches an expression and if the value of the expression changes it calls its notify handler.
The example uses GtkExpressionWatch in the line 104 to 107.
expression1 = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_WINDOW, NULL, "default-width");
watch_width = gtk_expression_watch (expression1, win1, notify, NULL, NULL);
expression2 = gtk_property_expression_new (GTK_TYPE_WINDOW, NULL, "default-height");
watch_height = gtk_expression_watch (expression2, win1, notify, NULL, NULL);
The expressions above refer to "default-width" and "default-height" properties of GtkWindow.
watch_width watches expression1.
The second argument win1 is this instance for expression1.
So, watch_width watches the value of "default-width" property of win1.
If the value changes, it calls notify handler.
The fourth and fifth arguments are NULL because no user data is necessary.
watch_height also connects notify handler to expression2.
So, notiry is called when "default-width" or "default-height" changes.
The handler norify is as follows.
1 static void
2 notify (gpointer user_data) {
3 GValue value = G_VALUE_INIT;
4 char *title;
5
6 if (watch_width && gtk_expression_watch_evaluate (watch_width, &value))
7 width = g_value_get_int (&value);
8 g_value_unset (&value);
9 if (watch_height && gtk_expression_watch_evaluate (watch_height, &value))
10 height = g_value_get_int (&value);
11 g_value_unset (&value);
12 title = g_strdup_printf ("%d x %d", width, height);
13 gtk_window_set_title (GTK_WINDOW (win1), title);
14 g_free (title);
15 }
- 6-11: Evaluates
expression1andexpression2withexpression_watch_evaluatefunction. - 12: Creates a string
title. It contains the width and height, for example, "800 x 600". - 13: Sets the title of
win1with the stringtitle.
The title of the window reflects the size of the window.
exp.ui
exp.c builds a GtkWindow instance win2 with exp.ui.
The ui file exp.ui includes tags to create GtkExpressions.
The tags are:
- constant tag to create constant expression
- lookup tag to create property expression
- closure tag to create closure expression
- binding tag to bind a property to an expression
The window win2 behaves like win1.
Because similar expressions are built with the ui file.
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2 <interface>
3 <object class="GtkWindow" id="win2">
4 <binding name="title">
5 <closure type="gchararray" function="set_title">
6 <lookup name="default-width" type="GtkWindow"></lookup>
7 <lookup name="default-height" type="GtkWindow"></lookup>
8 </closure>
9 </binding>
10 <property name="default-width">600</property>
11 <property name="default-height">400</property>
12 <child>
13 <object class="GtkBox">
14 <property name="orientation">GTK_ORIENTATION_VERTICAL</property>
15 <child>
16 <object class="GtkLabel">
17 <binding name="label">
18 <constant type="gint">100</constant>
19 </binding>
20 </object>
21 </child>
22 <child>
23 <object class="GtkLabel">
24 <binding name="label">
25 <lookup name="text">buffer</lookup>
26 </binding>
27 </object>
28 </child>
29 <child>
30 <object class="GtkLabel">
31 <binding name="label">
32 <lookup name="application-id">
33 <lookup name="application">win2</lookup>
34 </lookup>
35 </binding>
36 </object>
37 </child>
38 <child>
39 <object class="GtkEntry" id="entry">
40 <property name="buffer">
41 <object class="GtkEntryBuffer" id="buffer"></object>
42 </property>
43 </object>
44 </child>
45 </object>
46 </child>
47 </object>
48 </interface>
constant tag
A constant tag corresponds to a constant expression.
- 18: Constant tag. The constant expression is created with the tag. It returns 100 of which the type is gint when it is evaluated. The type gint is the same as int.
- 17-19: Binding tag corresponds to
gtk_expression_bindfunction.nameattribute specifies the "label" property of the GtkLabel object just before the binding tag. Binding tag uses the same GtkLabel object for athisobject to evaluate the expression. (But the constant expression doesn't use thethisobject at all.) The expression returns a int type GValue. On the other hand "label" property holds a string type GValue. When a GValue is copied to another GValue, the type is automatically converted if possible. In this case, an int100is converted to a string"100".
These binding and constant tag works. But they are not good. A property tag is more straightforward.
<object class="GtkLabel">
<property name="label">100</property>
</object>
This example just shows the way how to use constant tag. Constant tag is mainly used to give a constant argument to a closure.
lookup tag
A lookup tag corresponds to a property expression. Line 23 to 27 is copied here.
<object class="GtkLabel">
<binding name="label">
<lookup name="text">buffer</lookup>
</binding>
</object>
- binding tag binds a "label" property in GtkLabel to an expression. The expression is defined with a lookup tag.
- The lookup tag defines a property expression looks up a "text" property in
bufferinstance. Thebufferinstance is defined in the line 41. It is a GtkEntryBuffer belongs to a GtkEntryentry. A lookup tag takes an object in some ways to look up for a property.- If it has no contents, it takes
thisinstance when it is evaluated. - If it has a content of a tag for an expression, which is constant, lookup or closure tag, the value of the expression will be the object to look up when it is evaluated.
- If it has a content of an id of an object, then the instance of the object will be taken as the object to lookup.
- If it has no contents, it takes
As a result, the label of the GtkLabel instance are bound to the text in the field of GtkEntry. If a user input a text in the field, GtkLabel displays the same text.
Another lookup tag is in the lines from 30 to 36.
<object class="GtkLabel">
<binding name="label">
<lookup name="application-id">
<lookup name="application">win2</lookup>
</lookup>
</binding>
</object>
- Two expressions are nested.
- A lookup tag looks up "application-id" property of the next expression.
- The next lookup tag looks up "application" property of
win2instance.
As a result, the "label" property in the GtkLabel instance is bound to the "application-id" property. The nested tag makes a chain like:
"label" <= "application-id" <= "application" <= `win2`
closure tag
The lines from 3 to 9 include a closure tag.
<object class="GtkWindow" id="win2">
<binding name="title">
<closure type="gchararray" function="set_title">
<lookup name="default-width" type="GtkWindow"></lookup>
<lookup name="default-height" type="GtkWindow"></lookup>
</closure>
</binding>
- A binding tag corresponds to a
gtk_expression_bindfunction.nameattribute specifies the "title" property ofwin2. Binding tag giveswin2as thethisobject to the expressions, which are the contents of the binding tag. So, closure tag and lookup tags usewin2as thethisobject when they are evaluated. - A closure tag corresponds to a closure expression.
Its callback function is
set_titleand it returns "gchararray" type, which is "an array of characters" i.e. a string. The contents of the closure tag are assigned to parameters of the function. So,set_titlehas three parameters,win2(thisobject), default width and default height. - Lookup tags correspond to property expressions.
They lookup "default-width" and "default-height" properties of
win2(thisobject). - Binding tab creates GtkExpressionWatch automatically, so "title" property reflects the changes of "default-width" and "default-height" properties.
set_title function in exp.c is as follows.
1 char *
2 set_title (GtkWidget *win, int width, int height) {
3 return g_strdup_printf ("%d x %d", width, height);
4 }
It just creates a string, for example, "800 x 600", and returns it.
You've probably been notice that ui file is easier and clearer than the corresponding function definitions. One of the most useful case of GtkExpression is building GtkListItem instance with GtkBuilderListItemFatory. Such case has already been described in the prior two sections.
It will be used in the next section to build GtkListItem in GtkColumnView, which is the most useful view object for GListModel.
Compilation and execution
All the sources are in src/expression directory. Change your current directory to the directory above and run meson and ninja. Then, execute the application.
$ meson _build
$ ninja -C _build
$ build/exp
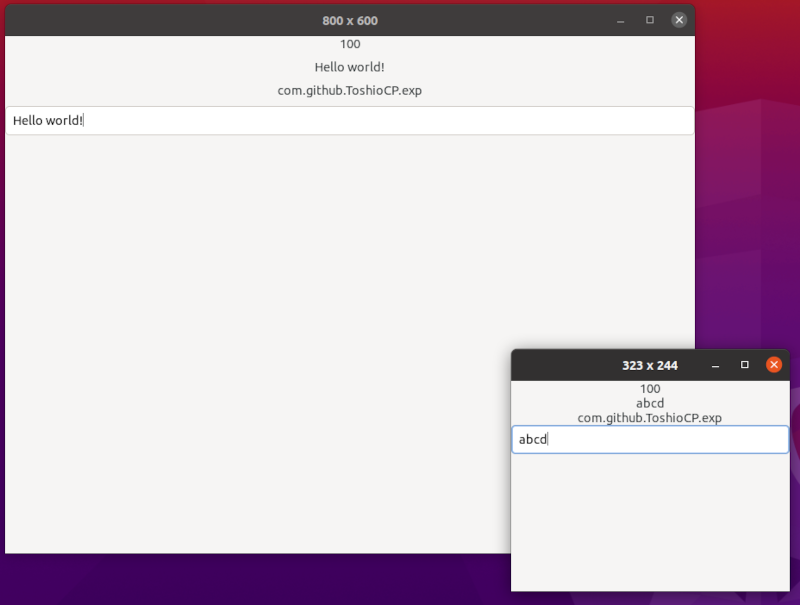
Then, two windows appear.
If you put some text in the field of the entry, then the same text appears in the second GtkLabel. Because the "label" property of the second GtkLabel instance is bound to the text in the GtkEntryBuffer.
If you resize the window, then the size appears in the title bar because the "title" property is bound to "default^width" and "default-height" properties.
Up: Readme.md, Prev: Section 25