14 KiB
Up: README.md, Prev: Section 7, Next: Section 9
Defining a child object
A very simple editor
In the previous section we made a very simple file viewer. Now we go on to rewrite it and turn it into very simple editor. Its source file is in tfe1.c (text file editor 1).
GtkTextView has a feature for editing multiple lines. Therefore, we don't need to write the program from scratch, we just add two things to the file viewer:
- Memory to store a pointer to the GFile instance.
- A function to write the file.
There are a couple of ways to store the details of GFile.
- Use global variables; or
- Make a child object, which can extend the instance memory for the GFile object.
Using global variables is easy to implement. Define a sufficient size array of pointers to GFile. For example,
GFile *f[20];
The variable f[i] corresponds to the file associated to the i-th GtkNotebookPage.
There are however two problems with this.
The first concerns the size of the array.
If a user gives too many arguments (more than 20 in the example above), it is impossible to store the additional pointers to the GFile instances.
The second is the increasing difficulty for maintenance of the program.
We have a small program so far,
but however, if you continue developing it, the size of the program will grow.
Generally speaking, the bigger the program size, the more difficult it is to keep track of and maintain global variables. Global variables can be used and changed anywhere throughout the entire program.
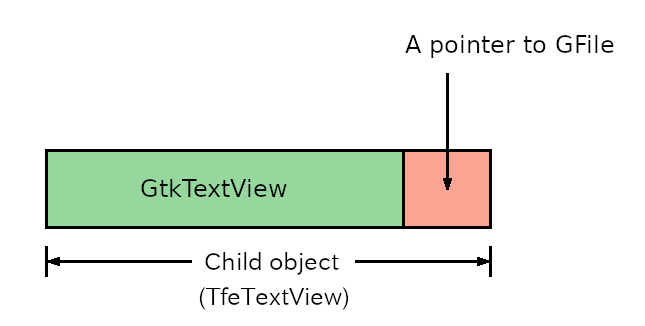
Making a child object is a good idea in terms of maintenance. One thing you need to be careful of is the difference between "child object" and "child widget". Here we are describing a "child object". A child object includes, and expands on its parent object, as a child object derives everything from the parent object.
We will define TfeTextView as a child object of GtkTextView. It has everything that GtkTextView has. Specifically, TfeTextView has a GtkTextbuffer which corresponds to the GtkTextView inside TfeTextView. The additional important thing is that TfeTextView can also keep an additional pointer to GFile.
In general, this is how GObjects work. Understanding the general theory about Gobject's is difficult, particularly for beginners. So, I will just show you the way how to write the code and avoid the theoretical side. If you want to know about GObject system, refer to another tutorial.
How to define a child object of GtkTextView
Let's define the TfeTextView object, which is a child object of GtkTextView. First, look at the program below.
#define TFE_TYPE_TEXT_VIEW tfe_text_view_get_type ()
G_DECLARE_FINAL_TYPE (TfeTextView, tfe_text_view, TFE, TEXT_VIEW, GtkTextView)
struct _TfeTextView
{
GtkTextView parent;
GFile *file;
};
G_DEFINE_TYPE (TfeTextView, tfe_text_view, GTK_TYPE_TEXT_VIEW);
static void
tfe_text_view_init (TfeTextView *tv) {
}
static void
tfe_text_view_class_init (TfeTextViewClass *class) {
}
void
tfe_text_view_set_file (TfeTextView *tv, GFile *f) {
tv -> file = f;
}
GFile *
tfe_text_view_get_file (TfeTextView *tv) {
return tv -> file;
}
GtkWidget *
tfe_text_view_new (void) {
return GTK_WIDGET (g_object_new (TFE_TYPE_TEXT_VIEW, NULL));
}
If you are curious about the background theory of this program, that's good, because knowing the theory is very important if you want to program GTK applications. Look at GObject API Reference. All you need is described there, or refer to GObject tutorial. It's a tough journey especially for beginners so for now, you don't need to know about this difficult theory. It is enough to just remember the instructions below.
- TfeTextView is divided into two parts. Tfe and TextView. Tfe is called the prefix, namespace or module. TextView is called the object.
- There are three differnet identifier patterns. TfeTextView (camel case), tfe_text_view (this is used to write functions) and TFE_TEXT_VIEW (This is used to cast a pointer to point TfeTextView type).
- First, define TFE_TYPE_TEXT_VIEW macro as tfe_text_view_get_type (). The name is always (prefix)_TYPE_(object) and the letters are upper case. And the replacement text is always (prefix)_(object)_get_type () and the letters are lower case.
- Next, use G_DECLARE_FINAL_TYPE macro. The arguments are the child object name in camel case, lower case with underscore, prefix (upper case), object (upper case with underscore) and parent object name (camel case).
- Declare the structure _TfeTextView. The underscore is necessary. The first member is the parent object. Notice this is not a pointer but the object itself. The second member and after are members of the child object. TfeTextView structure has a pointer to a GFile instance as a member.
- Use G_DEFINE_TYPE macro. The arguments are the child object name in camel case, lower case with underscore and parent object type (prefix)_TYPE_(module).
- Define instance init function (tfe_text_view_init). Usually you don't need to do anything.
- Define class init function (tfe_text_view_class_init). You don't need to do anything in this object.
- Write function codes you want to add (tfe_text_view_set_file and tfe_text_view_get_file).
tvis a pointer to the TfeTextView object instance which is a C-structure declared with the tag _TfeTextView. So, the structure has a memberfileas a pointer to a GFile instance.tv->file = fis an assignment offto a memberfileof the structure pointed bytv. This is an example how to use the extended memory in a child widget. - Write a function to create an instance. Its name is (prefix)_(object)_new. If the parent object function needs parameters, this function also need them. You sometimes might want to add some parameters. It's your choice. Use g_object_new function to create the instance. The arguments are (prefix)_TYPE_(object), a list to initialize properties and NULL. In this code no property needs to be initialized. And the return value is casted to GtkWidget.
This program is not perfect. It has some problems. It will be modified later.
Close-request signal
Imagine that you are using this editor. First, you run the editor with arguments. The arguments are filenames. The editor reads the files and shows the window with the text of files in it. Then you edit the text. After you finish editing, you exit the editor. The editor updates files just before the window closes.
GtkWindow emits the "close-request" signal before it closes.
We connect the signal and the handler before_close.
A handler is a C function.
When a function is connected to a certain signal, we call it a handler.
The function before_close is invoked when the signal "close-request" is emitted.
g_signal_connect (win, "close-request", G_CALLBACK (before_close), NULL);
The argument win is a GtkApplicationWindow, in which the signal "close-request" is defined, and before_close is the handler.
G_CALLBACK cast is necessary for the handler.
The program of before_close is as follows.
1 static gboolean
2 before_close (GtkWindow *win, gpointer user_data) {
3 GtkWidget *nb = GTK_WIDGET (user_data);
4 GtkWidget *scr;
5 GtkWidget *tv;
6 GFile *file;
7 char *pathname;
8 GtkTextBuffer *tb;
9 GtkTextIter start_iter;
10 GtkTextIter end_iter;
11 char *contents;
12 unsigned int n;
13 unsigned int i;
14
15 n = gtk_notebook_get_n_pages (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb));
16 for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
17 scr = gtk_notebook_get_nth_page (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb), i);
18 tv = gtk_scrolled_window_get_child (GTK_SCROLLED_WINDOW (scr));
19 file = tfe_text_view_get_file (TFE_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
20 tb = gtk_text_view_get_buffer (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
21 gtk_text_buffer_get_bounds (tb, &start_iter, &end_iter);
22 contents = gtk_text_buffer_get_text (tb, &start_iter, &end_iter, FALSE);
23 if (! g_file_replace_contents (file, contents, strlen (contents), NULL, TRUE, G_FILE_CREATE_NONE, NULL, NULL, NULL)) {
24 pathname = g_file_get_path (file);
25 g_print ("ERROR : Can't save %s.", pathname);
26 g_free (pathname);
27 }
28 g_free (contents);
29 }
30 return FALSE;
31 }
The numbers on the left of items are line numbers in the source code.
- 15: Gets the number of pages
nbhas. - 16-29: For loop with regard to the index to each pages.
- 17-19: Gets GtkScrolledWindow, TfeTextView and a pointer to GFile.
The pointer was stored when
app_openhandler had run. It will be shown later. - 20-22: Gets GtkTextBuffer and contents.
start_iterandend_iterare iterators of the buffer. I don't want to explain them now because it would take a lot of time. Just remember these lines for the present. - 23-27: Writes the contents to the file. If it fails, it outputs an error message.
- 28: Frees
contents.
Source code of tfe1.c
The following is the complete source code of tfe1.c.
1 #include <gtk/gtk.h>
2
3 /* Define TfeTextView Widget which is the child object of GtkTextView */
4
5 #define TFE_TYPE_TEXT_VIEW tfe_text_view_get_type ()
6 G_DECLARE_FINAL_TYPE (TfeTextView, tfe_text_view, TFE, TEXT_VIEW, GtkTextView)
7
8 struct _TfeTextView
9 {
10 GtkTextView parent;
11 GFile *file;
12 };
13
14 G_DEFINE_TYPE (TfeTextView, tfe_text_view, GTK_TYPE_TEXT_VIEW);
15
16 static void
17 tfe_text_view_init (TfeTextView *tv) {
18 }
19
20 static void
21 tfe_text_view_class_init (TfeTextViewClass *class) {
22 }
23
24 void
25 tfe_text_view_set_file (TfeTextView *tv, GFile *f) {
26 tv -> file = f;
27 }
28
29 GFile *
30 tfe_text_view_get_file (TfeTextView *tv) {
31 return tv -> file;
32 }
33
34 GtkWidget *
35 tfe_text_view_new (void) {
36 return GTK_WIDGET (g_object_new (TFE_TYPE_TEXT_VIEW, NULL));
37 }
38
39 /* ---------- end of the definition of TfeTextView ---------- */
40
41 static gboolean
42 before_close (GtkWindow *win, gpointer user_data) {
43 GtkWidget *nb = GTK_WIDGET (user_data);
44 GtkWidget *scr;
45 GtkWidget *tv;
46 GFile *file;
47 char *pathname;
48 GtkTextBuffer *tb;
49 GtkTextIter start_iter;
50 GtkTextIter end_iter;
51 char *contents;
52 unsigned int n;
53 unsigned int i;
54
55 n = gtk_notebook_get_n_pages (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb));
56 for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
57 scr = gtk_notebook_get_nth_page (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb), i);
58 tv = gtk_scrolled_window_get_child (GTK_SCROLLED_WINDOW (scr));
59 file = tfe_text_view_get_file (TFE_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
60 tb = gtk_text_view_get_buffer (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
61 gtk_text_buffer_get_bounds (tb, &start_iter, &end_iter);
62 contents = gtk_text_buffer_get_text (tb, &start_iter, &end_iter, FALSE);
63 if (! g_file_replace_contents (file, contents, strlen (contents), NULL, TRUE, G_FILE_CREATE_NONE, NULL, NULL, NULL)) {
64 pathname = g_file_get_path (file);
65 g_print ("ERROR : Can't save %s.", pathname);
66 g_free (pathname);
67 }
68 g_free (contents);
69 }
70 return FALSE;
71 }
72
73 static void
74 app_activate (GApplication *app, gpointer user_data) {
75 g_print ("You need to give filenames as arguments.\n");
76 }
77
78 static void
79 app_open (GApplication *app, GFile ** files, gint n_files, gchar *hint, gpointer user_data) {
80 GtkWidget *win;
81 GtkWidget *nb;
82 GtkWidget *lab;
83 GtkNotebookPage *nbp;
84 GtkWidget *scr;
85 GtkWidget *tv;
86 GtkTextBuffer *tb;
87 char *contents;
88 gsize length;
89 char *filename;
90 int i;
91
92 win = gtk_application_window_new (GTK_APPLICATION (app));
93 gtk_window_set_title (GTK_WINDOW (win), "file editor");
94 gtk_window_maximize (GTK_WINDOW (win));
95
96 nb = gtk_notebook_new ();
97 gtk_window_set_child (GTK_WINDOW (win), nb);
98
99 for (i = 0; i < n_files; i++) {
100 if (g_file_load_contents (files[i], NULL, &contents, &length, NULL, NULL)) {
101 scr = gtk_scrolled_window_new ();
102 tv = tfe_text_view_new ();
103 tb = gtk_text_view_get_buffer (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv));
104 gtk_text_view_set_wrap_mode (GTK_TEXT_VIEW (tv), GTK_WRAP_WORD_CHAR);
105 gtk_scrolled_window_set_child (GTK_SCROLLED_WINDOW (scr), tv);
106
107 tfe_text_view_set_file (TFE_TEXT_VIEW (tv), g_file_dup (files[i]));
108 gtk_text_buffer_set_text (tb, contents, length);
109 g_free (contents);
110 filename = g_file_get_basename (files[i]);
111 lab = gtk_label_new (filename);
112 gtk_notebook_append_page (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb), scr, lab);
113 nbp = gtk_notebook_get_page (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb), scr);
114 g_object_set (nbp, "tab-expand", TRUE, NULL);
115 g_free (filename);
116 } else if ((filename = g_file_get_path (files[i])) != NULL) {
117 g_print ("No such file: %s.\n", filename);
118 g_free (filename);
119 } else
120 g_print ("No valid file is given\n");
121 }
122 if (gtk_notebook_get_n_pages (GTK_NOTEBOOK (nb)) > 0) {
123 g_signal_connect (win, "close-request", G_CALLBACK (before_close), nb);
124 gtk_widget_show (win);
125 } else
126 gtk_window_destroy (GTK_WINDOW (win));
127 }
128
129 int
130 main (int argc, char **argv) {
131 GtkApplication *app;
132 int stat;
133
134 app = gtk_application_new ("com.github.ToshioCP.tfe1", G_APPLICATION_HANDLES_OPEN);
135 g_signal_connect (app, "activate", G_CALLBACK (app_activate), NULL);
136 g_signal_connect (app, "open", G_CALLBACK (app_open), NULL);
137 stat =g_application_run (G_APPLICATION (app), argc, argv);
138 g_object_unref (app);
139 return stat;
140 }
- 107: Sets the pointer to GFile into TfeTextView.
files[i]is a pointer to GFile structure. It will be freed by the system. So you need to copy it.g_file_dupduplicates the given GFile structure. - 123: Connects "close-request" signal and
before_closehandler. The fourth argument is called user data and it is given to the signal handler. So,nbis given tobefore_closeas the second argument.
Now compile and run it.
There's a sample file in the directory tfe.
Type ./a.out taketori.txt.
Modify the contents and close the window.
Make sure that the file is modified.
Now we got a very simple editor. It's not smart. We need more features like open, save, saveas, change font and so on. We will add them in the next section and after.