19 KiB
Up: README.md, Prev: Section 19, Next: Section 21
Composite widgets and alert dialog
The source files are in the Gtk4 tutorial GitHub repository.
Download it and see src/tfe6 directory.
An outline of new Tfe text editor
Tfe text editor will be restructured. The program is divided into six parts.
- Main program: the C main function.
- TfeApplication object: It is like GtkApplication but keeps GSettings and CSS Provider.
- TfeWindow object: It is a window with buttons and a notebook.
- TfePref object: A preference dialog.
- TfeAlert object: An alert dialog.
- pdf2css.h and pdf2css.c: Font and CSS utility functions.
This section describes TfeAlert. Others will be explained in the following sections.
Composite widgets
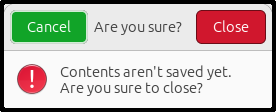
The alert dialog is like this:
Tfe uses it when a user quits the application or closes a notebook without saving data to files.
The dialog has a title, buttons, an icon and a message. Therefore, it consists of several widgets. Such dialog is called a composite widget.
Composite widgets are defined with template XMLs. The class is built in the class initialization function and the instances are built and desposed by the following functions.
- gtk_widget_init_template
- gtk_widget_dispose_template
TfeAlert is a good example to know composite widgets. It is defined with the three files.
- tfealert.ui: XML file
- tfealert.h: Header file
- tfealert.c: C program file
The XML file
A template tag is used in a composite widget XML.
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2 <interface>
3 <template class="TfeAlert" parent="GtkWindow">
4 <property name="resizable">FALSE</property>
5 <property name="modal">TRUE</property>
6 <property name="titlebar">
7 <object class="GtkHeaderBar">
8 <property name="show-title-buttons">FALSE</property>
9 <property name="title-widget">
10 <object class="GtkLabel" id="lb_title">
11 <property name="label">Are you sure?</property>
12 <property name="single-line-mode">True</property>
13 </object>
14 </property>
15 <child type="start">
16 <object class="GtkButton" id="btn_cancel">
17 <property name="label">Cancel</property>
18 <style>
19 <class name="suggested-action"/>
20 </style>
21 <signal name="clicked" handler="cancel_cb" swapped="TRUE" object="TfeAlert"></signal>
22 </object>
23 </child>
24 <child type="end">
25 <object class="GtkButton" id="btn_accept">
26 <property name="label">Close</property>
27 <style>
28 <class name="destructive-action"/>
29 </style>
30 <signal name="clicked" handler="accept_cb" swapped="TRUE" object="TfeAlert"></signal>
31 </object>
32 </child>
33 </object>
34 </property>
35 <child>
36 <object class="GtkBox">
37 <property name="orientation">GTK_ORIENTATION_HORIZONTAL</property>
38 <property name="spacing">12</property>
39 <property name="margin-top">12</property>
40 <property name="margin-bottom">12</property>
41 <property name="margin-start">12</property>
42 <property name="margin-end">12</property>
43 <child>
44 <object class="GtkImage">
45 <property name="icon-name">dialog-warning</property>
46 <property name="icon-size">GTK_ICON_SIZE_LARGE</property>
47 </object>
48 </child>
49 <child>
50 <object class="GtkLabel" id="lb_message">
51 </object>
52 </child>
53 </object>
54 </child>
55 </template>
56 </interface>
57
- 3: A template tag defines a composite widget. The class attribute tells the class name of the composite widget. The parent attribute tells the parent class of the composite widget. So, TfeAlert is a child class of GtkWindow. A parent attribute is an option and you can leave it out. But it is recommended to write it in the template tag.
- 4-6: Its three properties are defined. These properties are inherited from GtkWindow. The titlebar property has a widget for a custom title bar. The typical widget is GtkHeaderBar.
- 8: If the property "show-title-buttons" is TRUE, the title buttons like close, minimize and maximize are shown. Otherwise it is not shown. The TfeAlert object is not resizable. It is closed when either of the two buttons, cancel or accept, is clicked. Therefore the title buttons are not necessary and this property is set to FALSE.
- 9-14: The bar has a title, which is a GtkLabel widget. The default title is "Are you sure?" but it can be replaced by an instance method.
- 15-32: The bar has two buttons, cancel and accept.
The cancel button is on the left so the child tag has
type="start"attribute. The accept button is on the right so the child tag hastype="end"attribute. The dialog is shown when the user clicked the close button or the quit menu without saving the data. Therefore, it is safer for the user to click on the cancel button of the alert dialog. So, the cancel button has a "suggested-action" CSS class. Ubuntu colors the button green but the color can be blue or other appropriate one defined by the system. In the same way the accept button has a "destructive-action" CSS class and is colored red. Two buttons have signals which are defined by the signal tags. - 35-54: A horizontal box has an image icon and a label.
- 44-47: The GtkImage widget displays an image. The "icon-name" property is an icon name in the icon theme. The theme depends on your system. You can check it with an icon browser.
$ gtk4-icon-browser
The "dialog-warning" icon is something like this.
These are made by my hand. The real image on the alert dialog is nicer.
It is possible to define the alert widget as a child of GtkDialog. But GtkDialog is deprecated since GTK version 4.10. And users should use GtkWindow instead of GtkDialog.
The header file
The header file is similar to the one of TfeTextView.
1 #pragma once
2
3 #include <gtk/gtk.h>
4
5 #define TFE_TYPE_ALERT tfe_alert_get_type ()
6 G_DECLARE_FINAL_TYPE (TfeAlert, tfe_alert, TFE, ALERT, GtkWindow)
7
8 /* "response" signal id */
9 enum TfeAlertResponseType
10 {
11 TFE_ALERT_RESPONSE_ACCEPT,
12 TFE_ALERT_RESPONSE_CANCEL
13 };
14
15 const char *
16 tfe_alert_get_title (TfeAlert *alert);
17
18 const char *
19 tfe_alert_get_message (TfeAlert *alert);
20
21 const char *
22 tfe_alert_get_button_label (TfeAlert *alert);
23
24 void
25 tfe_alert_set_title (TfeAlert *alert, const char *title);
26
27 void
28 tfe_alert_set_message (TfeAlert *alert, const char *message);
29
30 void
31 tfe_alert_set_button_label (TfeAlert *alert, const char *btn_label);
32
33 GtkWidget *
34 tfe_alert_new (void);
35
36 GtkWidget *
37 tfe_alert_new_with_data (const char *title, const char *message, const char* btn_label);
- 5-6: These two lines are always needed to define a new object.
TFE_TYPE_ALERTis the type of TfeAlert object and it is a macro expanded intotfe_alert_get_type (). G_DECLARE_FINAL_TYPE macro is expanded into:- The declaration of the function
tfe_alert_get_type TfeAlertis defined as a typedef ofstruct _TfeAlert, which is defined in the C file.TFE_ALERTandTFE_IS_ALERTmacro is defined as a cast and type check function.TfeAlertClassstructure is defined as a final class.
- The declaration of the function
- 8-13: The TfeAlert class has a "response" signal.
It has a parameter and the parameter type is defined as a
TfeAlertResponseTypeenumerative constant. - 15-31: Getter and setter methods.
- 33-37: Functions to create a instance.
The function
tfe_alert_new_with_datais a convenience function, which creates an instance and sets data at once.
The C file
Functions for composite widgets
The following codes are extracted from tfealert.c.
#include <gtk/gtk.h>
#include "tfealert.h"
struct _TfeAlert {
GtkWindow parent;
GtkLabel *lb_title;
GtkLabel *lb_message;
GtkButton *btn_accept;
GtkButton *btn_cancel;
};
G_DEFINE_FINAL_TYPE (TfeAlert, tfe_alert, GTK_TYPE_WINDOW);
static void
cancel_cb (TfeAlert *alert) {
... ... ...
}
static void
accept_cb (TfeAlert *alert) {
... ... ...
}
static void
tfe_alert_dispose (GObject *gobject) { // gobject is actually a TfeAlert instance.
gtk_widget_dispose_template (GTK_WIDGET (gobject), TFE_TYPE_ALERT);
G_OBJECT_CLASS (tfe_alert_parent_class)->dispose (gobject);
}
static void
tfe_alert_init (TfeAlert *alert) {
gtk_widget_init_template (GTK_WIDGET (alert));
}
static void
tfe_alert_class_init (TfeAlertClass *class) {
G_OBJECT_CLASS (class)->dispose = tfe_alert_dispose;
gtk_widget_class_set_template_from_resource (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), "/com/github/ToshioCP/tfe/tfealert.ui");
gtk_widget_class_bind_template_child (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), TfeAlert, lb_title);
gtk_widget_class_bind_template_child (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), TfeAlert, lb_message);
gtk_widget_class_bind_template_child (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), TfeAlert, btn_accept);
gtk_widget_class_bind_template_child (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), TfeAlert, btn_cancel);
gtk_widget_class_bind_template_callback (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), cancel_cb);
gtk_widget_class_bind_template_callback (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), accept_cb);
... ... ...
}
GtkWidget *
tfe_alert_new (void) {
return GTK_WIDGET (g_object_new (TFE_TYPE_ALERT, NULL));
}
- The macro
G_DEFINE_FINAL_TYPEis available since GLib version 2.70. It is used only for a final type class. You can useG_DEFINE_TYPEmacro instead. They are expanded into:- The declaration of the functions
tfe_alert_initandtfe_alert_class_init. They are defined in the following part of the C program. - The definition of the variable
tfe_alert_parent_class. - The definition of the function
tfe_alert_get_type.
- The declaration of the functions
- The names of the members of
_TfeAlert, which arelb_title,lb_message,btn_acceptandbtn_cancel, must be the same as the id attribute in the XML filetfealert.ui. - The function
tfe_alert_class_initinitializes the composite widget class.- The function
gtk_widget_class_set_template_from_resourcesets the template of the class. The template is built from the XML resource "tfealert.ui". At this moment no instance is created. It just makes the class recognize the structure of the object. That’s why the top level tag is not object but template in the XML file. - The function macro
gtk_widget_class_bind_template_childconnects the member of TfeAlert and the object class in the template. So, for example, you can access tolb_titleGtkLabel instance viaalert->lb_titlewherealertis an instance of TfeAlert class. - The function
gtk_widget_class_bind_template_callbackconnects the callback function and thehandlerattribute of the signal tag in the XML. For example, the "clicked" signal on the cancel button has a handler named "cancel_cb" in the signal tag. And the functioncancel_cbexists in the C file above. These two are connected so when the signal is emitted the functioncancel_cbis called. You can addstaticstorage class to the callback function thanks to this connection.
- The function
- The function
tfe_alert_initinitializes the newly created instance. You need to callgtk_widget_init_templateto create and initialize the child widgets in the template. - The function
tfe_alert_desposereleases objects. The functiongtk_widget_despose_templateclears the template children. - The function
tfe_alert_newcreates the composite widget TfeAlert instance. It creates not only TfeAlert itself but also all the child widgets that the composite widget has.
Other functions
The following is the full codes of tfealert.c.
1 #include <gtk/gtk.h>
2 #include "tfealert.h"
3
4 struct _TfeAlert {
5 GtkWindow parent;
6 GtkLabel *lb_title;
7 GtkLabel *lb_message;
8 GtkButton *btn_accept;
9 GtkButton *btn_cancel;
10 };
11
12 G_DEFINE_FINAL_TYPE (TfeAlert, tfe_alert, GTK_TYPE_WINDOW);
13
14 enum {
15 RESPONSE,
16 NUMBER_OF_SIGNALS
17 };
18
19 static guint tfe_alert_signals[NUMBER_OF_SIGNALS];
20
21 static void
22 cancel_cb (TfeAlert *alert) {
23 g_signal_emit (alert, tfe_alert_signals[RESPONSE], 0, TFE_ALERT_RESPONSE_CANCEL);
24 gtk_window_destroy (GTK_WINDOW (alert));
25 }
26
27 static void
28 accept_cb (TfeAlert *alert) {
29 g_signal_emit (alert, tfe_alert_signals[RESPONSE], 0, TFE_ALERT_RESPONSE_ACCEPT);
30 gtk_window_destroy (GTK_WINDOW (alert));
31 }
32
33 const char *
34 tfe_alert_get_title (TfeAlert *alert) {
35 return gtk_label_get_text (alert->lb_title);
36 }
37
38 const char *
39 tfe_alert_get_message (TfeAlert *alert) {
40 return gtk_label_get_text (alert->lb_message);
41 }
42
43 const char *
44 tfe_alert_get_button_label (TfeAlert *alert) {
45 return gtk_button_get_label (alert->btn_accept);
46 }
47
48 void
49 tfe_alert_set_title (TfeAlert *alert, const char *title) {
50 gtk_label_set_text (alert->lb_title, title);
51 }
52
53 void
54 tfe_alert_set_message (TfeAlert *alert, const char *message) {
55 gtk_label_set_text (alert->lb_message, message);
56 }
57
58 void
59 tfe_alert_set_button_label (TfeAlert *alert, const char *btn_label) {
60 gtk_button_set_label (alert->btn_accept, btn_label);
61 }
62
63 static void
64 tfe_alert_dispose (GObject *gobject) { // gobject is actually a TfeAlert instance.
65 gtk_widget_dispose_template (GTK_WIDGET (gobject), TFE_TYPE_ALERT);
66 G_OBJECT_CLASS (tfe_alert_parent_class)->dispose (gobject);
67 }
68
69 static void
70 tfe_alert_init (TfeAlert *alert) {
71 gtk_widget_init_template (GTK_WIDGET (alert));
72 }
73
74 static void
75 tfe_alert_class_init (TfeAlertClass *class) {
76 G_OBJECT_CLASS (class)->dispose = tfe_alert_dispose;
77 gtk_widget_class_set_template_from_resource (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), "/com/github/ToshioCP/tfe/tfealert.ui");
78 gtk_widget_class_bind_template_child (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), TfeAlert, lb_title);
79 gtk_widget_class_bind_template_child (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), TfeAlert, lb_message);
80 gtk_widget_class_bind_template_child (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), TfeAlert, btn_accept);
81 gtk_widget_class_bind_template_child (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), TfeAlert, btn_cancel);
82 gtk_widget_class_bind_template_callback (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), cancel_cb);
83 gtk_widget_class_bind_template_callback (GTK_WIDGET_CLASS (class), accept_cb);
84
85 tfe_alert_signals[RESPONSE] = g_signal_new ("response",
86 G_TYPE_FROM_CLASS (class),
87 G_SIGNAL_RUN_LAST | G_SIGNAL_NO_RECURSE | G_SIGNAL_NO_HOOKS,
88 0 /* class offset */,
89 NULL /* accumulator */,
90 NULL /* accumulator data */,
91 NULL /* C marshaller */,
92 G_TYPE_NONE /* return_type */,
93 1 /* n_params */,
94 G_TYPE_INT
95 );
96 }
97
98 GtkWidget *
99 tfe_alert_new (void) {
100 return GTK_WIDGET (g_object_new (TFE_TYPE_ALERT, NULL));
101 }
102
103 GtkWidget *
104 tfe_alert_new_with_data (const char *title, const char *message, const char* btn_label) {
105 GtkWidget *alert = tfe_alert_new ();
106 tfe_alert_set_title (TFE_ALERT (alert), title);
107 tfe_alert_set_message (TFE_ALERT (alert), message);
108 tfe_alert_set_button_label (TFE_ALERT (alert), btn_label);
109 return alert;
110 }
The function tfe_alert_new_with_data is used more often than tfe_alert_new to create a new instance.
It creates the instance and sets three data at the same time.
The following is the common process when you use the TfeAlert class.
- Call
tfe_alert_new_with_dataand create an instance. - Call
gtk_window_set_transient_forto set the transient parent window. - Call
gtk_window_presentto show the TfeAlert dialog. - Connect "response" signal and a handler.
- The user clicks on the cancel or accept button. Then the dialog emits the "response" signal and destroy itself.
- The user catches the signal and do something.
The rest of the program is:
- 14-19: An array for a signal id. You can use a variable instead of an array because the class has only one signal. But using an array is a common way.
- 21-31: Signal handlers. They emits the "response" signal and destroy the instance itself.
- 33-61: Getters and setters.
- 85-95: Creates the "response" signal.
- 103-110: A convenience function
tfe_alert_new_with_datacreates an instance and sets labels.
An example
There's an example in the src/tfe6/example directory.
It shows how to use TfeAlert.
The program is src/example/ex_alert.c.
1 #include <gtk/gtk.h>
2 #include "../tfealert.h"
3
4 static void
5 alert_response_cb (TfeAlert *alert, int response, gpointer user_data) {
6 if (response == TFE_ALERT_RESPONSE_ACCEPT)
7 g_print ("%s\n", tfe_alert_get_button_label (alert));
8 else if (response == TFE_ALERT_RESPONSE_CANCEL)
9 g_print ("Cancel\n");
10 else
11 g_print ("Unexpected error\n");
12 }
13
14 static void
15 app_activate (GApplication *application) {
16 GtkWidget *alert;
17 char *title, *message, *btn_label;
18
19 title = "Example for TfeAlert"; message = "Click on Cancel or Accept button"; btn_label = "Accept";
20 alert = tfe_alert_new_with_data (title, message, btn_label);
21 g_signal_connect (TFE_ALERT (alert), "response", G_CALLBACK (alert_response_cb), NULL);
22 gtk_window_set_application (GTK_WINDOW (alert), GTK_APPLICATION (application));
23 gtk_window_present (GTK_WINDOW (alert));
24 }
25
26 static void
27 app_startup (GApplication *application) {
28 }
29
30 #define APPLICATION_ID "com.github.ToshioCP.example_tfe_alert"
31
32 int
33 main (int argc, char **argv) {
34 GtkApplication *app;
35 int stat;
36
37 app = gtk_application_new (APPLICATION_ID, G_APPLICATION_DEFAULT_FLAGS);
38 g_signal_connect (app, "startup", G_CALLBACK (app_startup), NULL);
39 g_signal_connect (app, "activate", G_CALLBACK (app_activate), NULL);
40 stat =g_application_run (G_APPLICATION (app), argc, argv);
41 g_object_unref (app);
42 return stat;
43 }
The "activate" signal handler app_activate initializes the alert dialog.
- A TfeAlert instance is created.
- Its "response" signal is connected to the handler
alert_response_cb. - TfeAlert class is a sub class of GtkWindow so it can be a top level window that is connected to an application instance.
The function
gtk_window_set_applicationdoes that. - The dialog is shown.
A user clicks on either the cancel button or the accept button.
Then, the "response" signal is emitted and the dialog is destroyed.
The signal handler alert_response_cb checks the response and prints "Accept" or "Cancel".
If an error happens, it prints "Unexpected error".
You can compile it with meson and ninja.
$ cd src/tfe6/example
$ meson setup _build
$ ninja -C _build
$ _build/ex_alert
Accept #<= if you clicked on the accept button
Up: README.md, Prev: Section 19, Next: Section 21