20 KiB
Up: Readme.md, Prev: Section 10, Next: Section 12
Initialization and destruction of instances
A new version of the text file editor (tfe) will be made in this section and the following four sections.
It is tfe5.
There are many changes from the prior version.
All the sources are listed in Section 16.
They are located in two directories, src/tfe5 and src/tfetextview.
Encapsulation
We've divided C source file into two parts. But it is not enough in terms of encapsulation.
tfe.cincludes everything other than TfeTextView. It should be divided at least into two parts,tfeapplication.candtfenotebook.c.- Header files also need to be organized.
However, first of all, I'd like to focus on the object TfeTextView.
It is a child object of GtkTextView and has a new member file in it.
The important thing is to manage the Gfile object pointed by file.
- What is necessary to GFile when creating (or initializing) TfeTextView?
- What is necessary to GFile when destructing TfeTextView?
- TfeTextView should read/write a file by itself or not?
- How it communicates with objects outside?
You need to know at least class, instance and signals before thinking about them. I will explain them in this section and the next section. After that I will explain:
- Organizing functions.
- How to use GtkFileChooserDialog
GObject and its children
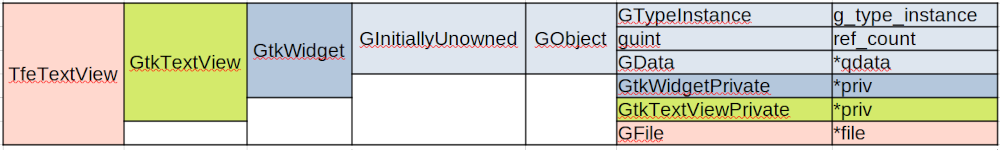
GObject and its children are objects, which have both class and instance. First, think about instance of objects. Instance is structured memory. THe structure is described as C language structure. The following is a structure of TfeTextView.
/* This typedef statement is automatically generated by the macro G_DECLARE_FINAL_TYPE */
typedef struct _TfeTextView TfeTextView;
struct _TfeTextView {
GtkTextView parent;
GFile *file;
};
The members of the structure are:
- The type of
parentis GtkTextView which is C structure. It is declared ingtktextview.h. GtkTextView is the parent of TfeTextView. fileis a pointer to GFile. It can be NULL if no file corresponds to the TfeTextView object.
Notice the program above is the declaration of the structure, not the definition.
So, no memories are allocated at this moment.
They are to be allocated when tfe_text_view_new function is invoked.
The memory allocated with tfe_text_view_new is an instance of TfeTextView object.
Therefore, There can be multiple TfeTextView instances if tfe_text_view_new is called multiple times.
You can find the declaration of the ancestors of TfeTextView in the source files of GTK and GLib. The following is extracts from the source files (not exactly the same).
typedef struct _GObject GObject;
typedef struct _GObject GInitiallyUnowned;
struct _GObject
{
GTypeInstance g_type_instance;
volatile guint ref_count;
GData *qdata;
};
typedef struct _GtkWidget GtkWidget;
struct _GtkWidget
{
GInitiallyUnowned parent_instance;
GtkWidgetPrivate *priv;
};
typedef struct _GtkTextView GtkTextView;
struct _GtkTextView
{
GtkWidget parent_instance;
GtkTextViewPrivate *priv;
};
In each structure, its parent is declared at the top of the members.
So, every ancestors is included in the child instance.
This is very important.
It guarantees a child widget to inherit all the features from ancestors.
The structure of TfeTextView is like the following diagram.
Initialization of a TfeTextView instance
The function tfe_text_view_new creates a new TfeTextView instance.
1 GtkWidget *
2 tfe_text_view_new (void) {
3 return GTK_WIDGET (g_object_new (TFE_TYPE_TEXT_VIEW, NULL));
4 }
When this function is involed, a TfeTextView instance is created and initialized. The initialization process is as follows.
- Initializes GObject (GInitiallyUnowned) part in TfeTextView instance.
- Initializes GtkWidget part in TfeTextView instance.
- Initializes GtkTextView part in TfeTextView instance.
- Initializes TfeTextView part in TfeTextView instance.
The step one through three is done by g_object_init, gtk_widget_init and gtk_text_view_init.
They are called by the system automatically and you don't need to care about them.
Step four is done by the function tfe_text_view_init in tfetextview.c.
1 static void
2 tfe_text_view_init (TfeTextView *tv) {
3 tv->file = NULL;
4 }
This function just initializes tv->file to be NULL.
Functions and Classes
In Gtk, all objects derived from GObject have class and instance (except abstract object). An instance is memory of C structure, which is described in the previous two subsections. Each object can have more than one instance. Those instances have the same structure. An instance just keeps status of the instance. Therefore, it is insufficient to define its behavior. We need at least two things. One is functions and the other is class.
You've already seen many functions.
For example, tfe_text_view_new is a function to create a TfeTextView instance.
These functions are similar to public object methods in object oriented languages such as Java or Ruby.
Functions are public, which means that they are expected to be used by other objects.
Class comprises mainly pointers to functions.
Those functions are used by the object itself or its descendant objects.
For example, GObject class is declared in gobject.h in GLib source files.
1 typedef struct _GObjectClass GObjectClass;
2 typedef struct _GObjectClass GInitiallyUnownedClass;
3
4 struct _GObjectClass
5 {
6 GTypeClass g_type_class;
7 /*< private >*/
8 GSList *construct_properties;
9 /*< public >*/
10 /* seldom overridden */
11 GObject* (*constructor) (GType type,
12 guint n_construct_properties,
13 GObjectConstructParam *construct_properties);
14 /* overridable methods */
15 void (*set_property) (GObject *object,
16 guint property_id,
17 const GValue *value,
18 GParamSpec *pspec);
19 void (*get_property) (GObject *object,
20 guint property_id,
21 GValue *value,
22 GParamSpec *pspec);
23 void (*dispose) (GObject *object);
24 void (*finalize) (GObject *object);
25 /* seldom overridden */
26 void (*dispatch_properties_changed) (GObject *object,
27 guint n_pspecs,
28 GParamSpec **pspecs);
29 /* signals */
30 void (*notify) (GObject *object,
31 GParamSpec *pspec);
32 /* called when done constructing */
33 void (*constructed) (GObject *object);
34 /*< private >*/
35 gsize flags;
36 /* padding */
37 gpointer pdummy[6];
38 };
39
I'd like to explain some of the members.
There's a pointer to the function dispose in line 23.
void (*dispose) (GObject *object);
The declaration is a bit complicated.
The asterisk before the identifier dispose means pointer.
So, the pointer dispose points to a function which has one parameter, which points a GObject structure, and returns no value.
In the same way, line 24 says finalize is a pointer to the function which has one parameter, which points a GObject structure, and returns no value.
void (*finalize) (GObject *object);
Look at the declaration of _GObjectClass so that you would find that most of the members are pointers to functions.
- 11: A function pointed by
constructoris called when the instance is generated. It completes the initialization of the instance. - 23: A function pointed by
disposeis called when the instance destructs itself. Destruction process is divided into two phases. The first one is called disposing. In this phase, the instance releases all the references to other instances. The second phase is finalizing. - 24: A function pointed by
finalizefinishes the destruction process. - The other pointers point to functions which are called while the instance lives.
These functions are called class methods. The methods are open to its descendants. But not open to the objects which are not the descendants.
TfeTextView class
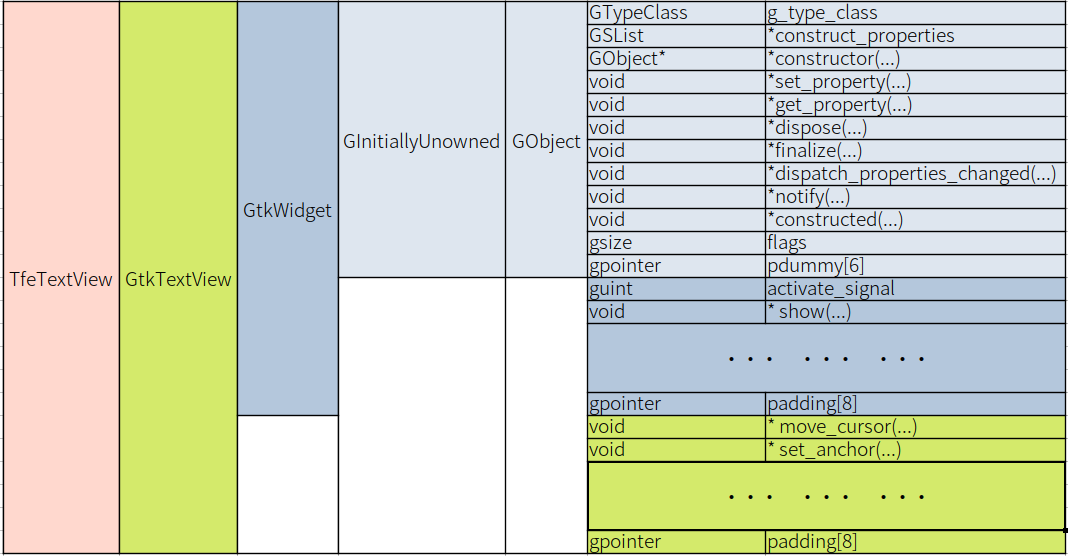
TfeTextView class is a structure and it includes all its ancestors' class in it.
typedef _TfeTextView TfeTextView;
struct _TfeTextView {
GtkTextView parent;
GFile *file;
};
TfeTextView structure has GtkTextView type as the first member. In the same way, GtkTextView has its parent type (GtkWidget) as the first member. GtkWidget has its parent type (GtkInitiallyUnowned) as the first member. The structure of GtkInitiallyUnowned is the same as GObject. Therefore, TFeTextView includes GObject, GtkWidget and GtkTextView in itself.
GObject -- GInitiallyUnowned -- GtkWidget -- GtkTextView -- TfeTextView
The following is extracts from the source files (not exactly the same).
1 struct _GtkWidgetClass
2 {
3 GInitiallyUnownedClass parent_class;
4
5 /*< public >*/
6
7 /* basics */
8 void (* show) (GtkWidget *widget);
9 void (* hide) (GtkWidget *widget);
10 void (* map) (GtkWidget *widget);
11 void (* unmap) (GtkWidget *widget);
12 void (* realize) (GtkWidget *widget);
13 void (* unrealize) (GtkWidget *widget);
14 void (* root) (GtkWidget *widget);
15 void (* unroot) (GtkWidget *widget);
16 void (* size_allocate) (GtkWidget *widget,
17 int width,
18 int height,
19 int baseline);
20 void (* state_flags_changed) (GtkWidget *widget,
21 GtkStateFlags previous_state_flags);
22 void (* direction_changed) (GtkWidget *widget,
23 GtkTextDirection previous_direction);
24
25 /* size requests */
26 GtkSizeRequestMode (* get_request_mode) (GtkWidget *widget);
27 void (* measure) (GtkWidget *widget,
28 GtkOrientation orientation,
29 int for_size,
30 int *minimum,
31 int *natural,
32 int *minimum_baseline,
33 int *natural_baseline);
34
35 /* Mnemonics */
36 gboolean (* mnemonic_activate) (GtkWidget *widget,
37 gboolean group_cycling);
38
39 /* explicit focus */
40 gboolean (* grab_focus) (GtkWidget *widget);
41 gboolean (* focus) (GtkWidget *widget,
42 GtkDirectionType direction);
43 void (* set_focus_child) (GtkWidget *widget,
44 GtkWidget *child);
45
46 /* keyboard navigation */
47 void (* move_focus) (GtkWidget *widget,
48 GtkDirectionType direction);
49 gboolean (* keynav_failed) (GtkWidget *widget,
50 GtkDirectionType direction);
51
52 gboolean (* query_tooltip) (GtkWidget *widget,
53 int x,
54 int y,
55 gboolean keyboard_tooltip,
56 GtkTooltip *tooltip);
57
58 void (* compute_expand) (GtkWidget *widget,
59 gboolean *hexpand_p,
60 gboolean *vexpand_p);
61
62 void (* css_changed) (GtkWidget *widget,
63 GtkCssStyleChange *change);
64
65 void (* system_setting_changed) (GtkWidget *widget,
66 GtkSystemSetting settings);
67
68 void (* snapshot) (GtkWidget *widget,
69 GtkSnapshot *snapshot);
70
71 gboolean (* contains) (GtkWidget *widget,
72 double x,
73 double y);
74
75 /*< private >*/
76
77 GtkWidgetClassPrivate *priv;
78
79 gpointer padding[8];
80 };
81
82 struct _GtkTextViewClass
83 {
84 GtkWidgetClass parent_class;
85
86 /*< public >*/
87
88 void (* move_cursor) (GtkTextView *text_view,
89 GtkMovementStep step,
90 int count,
91 gboolean extend_selection);
92 void (* set_anchor) (GtkTextView *text_view);
93 void (* insert_at_cursor) (GtkTextView *text_view,
94 const char *str);
95 void (* delete_from_cursor) (GtkTextView *text_view,
96 GtkDeleteType type,
97 int count);
98 void (* backspace) (GtkTextView *text_view);
99 void (* cut_clipboard) (GtkTextView *text_view);
100 void (* copy_clipboard) (GtkTextView *text_view);
101 void (* paste_clipboard) (GtkTextView *text_view);
102 void (* toggle_overwrite) (GtkTextView *text_view);
103 GtkTextBuffer * (* create_buffer) (GtkTextView *text_view);
104 void (* snapshot_layer) (GtkTextView *text_view,
105 GtkTextViewLayer layer,
106 GtkSnapshot *snapshot);
107 gboolean (* extend_selection) (GtkTextView *text_view,
108 GtkTextExtendSelection granularity,
109 const GtkTextIter *location,
110 GtkTextIter *start,
111 GtkTextIter *end);
112 void (* insert_emoji) (GtkTextView *text_view);
113
114 /*< private >*/
115
116 gpointer padding[8];
117 };
118
119 /* The following definition is generated by the macro G_DECLARE_FINAL_TYPE */
120 typedef struct {
121 GtkTextView parent_class;
122 } TfeTextViewClass;
123
- 120-122: This three lines are generated by the macro
G_DECLARE_FINAL_TYPE. So, they are not written in eithertfe_text_view.hortfe_text_view.c. - 3, 84, 121: Each derived class puts its parent class at the first member of its structure. It is the same as instance structures.
- Class members in ancestors are open to the descendant class.
So, they can be changed in
tfe_text_view_class_initfunction. For example, thedisposepointer in GObjectClass will be overridden later intfe_text_view_class_init. (Override is an object oriented programming terminology. Override is rewriting ancestors' class methods in the descendant class.) - Some class methods are often overridden.
set_property,get_property,dispose,finalizeandconstructedare such methods.
TfeTextViewClass includes its ancestors' class in it. It is illustrated in the following diagram.
Destruction of TfeTextView
Every Object derived from GObject has a reference count.
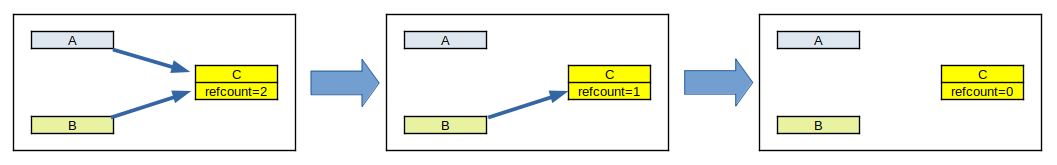
If an object A refers to an object B, then A keeps a pointer to B in A and at the same time increases the reference count of B by one with the function g_object_ref (B).
If A doesn't need B any longer, then A discards the pointer to B (usually it is done by assigning NULL to the pointer) and decreases the reference count of B by one with the function g_object_unref (B).
If two objects A and B refer to C, then the reference count of C is two. If A no longer needs C, A discards the pointer to C and decreases the reference count in C by one. Now the reference count of C is one. In the same way, if B no longer needs C, B discards the pointer to C and decreases the reference count in C by one. At this moment, no object refers to C and the reference count of C is zero. This means C is no longer useful. Then C destructs itself and finally the memories allocated to C is freed.
The idea above is based on an assumption that an object referred by nothing has reference count of zero.
When the reference count drops to zero, the object starts its destruction process.
The destruction process is split into two phases: disposing and finalizing.
In the disposing process, the object invokes the function pointed by dispose in its class to release all references to other objects.
In the finalizing process, it invokes the function pointed by finalize in its class to complete the destruction process.
These functions are also called handlers or methods.
For example, dispose handler or dispose method.
In the destruction process of TfeTextView, the reference count of widgets related to TfeTextView is automatically decreased.
But GFile pointed by tv->file needs to decrease its reference count by one.
You must write the code in the dispose handler tfe_text_view_dispose.
1 static void
2 tfe_text_view_dispose (GObject *gobject) {
3 TfeTextView *tv = TFE_TEXT_VIEW (gobject);
4
5 if (G_IS_FILE (tv->file))
6 g_clear_object (&tv->file);
7
8 G_OBJECT_CLASS (tfe_text_view_parent_class)->dispose (gobject);
9 }
- 5,6: If
tv->filepoints a GFile, decrease its reference count.g_clear_objectdecreases the reference count and assigns NULL totv->file. In dispose handlers, we usually useg_clear_objectrather thang_object_unref. - 8: invokes parent's dispose handler. (This will be explained later.)
In the disposing process, the object uses the pointer in its class to call the handler.
Therefore, tfe_text_view_dispose needs to be registered in the class when the TfeTextView class is initialized.
The function tfe_text_view_class_init is the class initialization function and it is declared in the replacement produced by G_DEFINE_TYPE macro.
static void
tfe_text_view_class_init (TfeTextViewClass *class) {
GObjectClass *object_class = G_OBJECT_CLASS (class);
object_class->dispose = tfe_text_view_dispose;
}
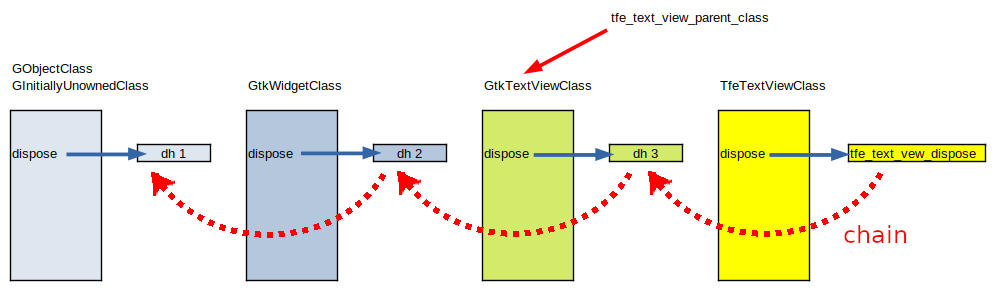
Each ancestors' class has been created before TfeTextViewClass is created.
Therefore, there are four classes and each class has a pointer to each dispose handler.
Look at the following diagram.
There are four classes -- GObjectClass (GInitiallyUnownedClass), GtkWidgetClass, GtkTextViewClass and TfeTextViewClass.
Each class has its own dispose handler -- dh1, dh2, dh3 and tfe_text_view_dispose.
Now, look at the tfe_text_view_dispose program above.
It first releases the reference to GFile object pointed by tv->file.
Then it invokes its parent's dispose handler in line 8.
G_OBJECT_CLASS (tfe_text_view_parent_class)->dispose (gobject);
tfe_text_view_parent_class,which is made by G_DEFINE_TYPE macro, is a pointer that points the parent object class.
Therefore, G_OBJECT_CLASS (tfe_text_view_parent_class)->dispose points the handler dh3 in the diagram above.
And gobject is a pointer to TfeTextView instance which is casted as a GObject instance.
dh3 releases all the references to objects in the GtkTextView part (it is actually the private area pointed by prev) in TfeTextView instance.
After that, dh3 calls dh2, and dh2 calls dh1.
Finally all the references are released.
Up: Readme.md, Prev: Section 10, Next: Section 12